James Powell
Ottawa’s Rink
18 January 1971
While Ottawa is a great place to live, even its most partisan citizens would have to agree that at life’s great banquet, it got a double helping of winter. On average, Ottawa receives roughly two metres of snow each year over a season that lasts from early November to well into April, with temperatures dipping to -30 Celsius. Consequently, to live happily in Ottawa, it’s important to embrace the season. Fortunately, we have access to lots of winter amenities, including wonderful ski trails and slopes in the Gatineau Hills just a short car ride away. But one of the city’s winter crown jewels is the Rideau Canal Skateway, which runs 7.8 kilometres through the heart of the city from the Ottawa River locks beside Parliament Hill to the Hartwell Locks at Carleton University. Each year, Ottawa citizens eagerly await the start of the winter skating season, checking regularly the National Capital Commission’s (NCC) web site or its information line on the state of the ice. Requiring an ice thickness of at least 30 centimetres, it takes at least a couple of weeks of temperatures persistently below -15 and a lot of hard work by NCC staff to prepare the ice surface before the Skateway can be safely opened to the public.
Typically, the skating season starts in early January and remains open until mid-March, though the Canal might close for short periods owing to temporary thaws. The earliest opening date occurred on 18 December 1971 and 1982. Its latest closing date was 25 March 1972. The average season is about 50 days, of which 42 are skating days. The longest season was 1971-72 with 95 days, while the shortest was 2015-16 with 34 days, of which only 18 were skating days. Even then, the skateway was open for its entire length for ony a few days. In contrast, the canal was open for a record 59 consecutive days during the previous 2014-15 season, attracting an estimated 1.2 million visitors. In general, however, shorter and milder winters associated with climate change is shortening the skating season.
Skating on the Canal has in fact been a feature of the City’s winters since the 19th century. In March 1874, The Globe newspaper reported that there “was good skating on the Rideau Canal.” The ribbon of ice running through the city beckoned youngsters of all ages when climatic conditions were just right for a smooth, solid ice surface to form—low temperatures for several days with little snow. When that happened, skaters would descend on the Canal to enjoy the ice. On one occasion early in the 20th century, it was reported that people could skate all the way from Lisgar Collegiate to Sunnyside without benefit of snowploughs or sweeping.
At best, however, the city tolerated impromptu skating on the Canal. When times became more litigious, it forbade it owing to the risk of injury, or even death. Although the water is partly drained from the Canal each fall, it is sufficiently deep in places for people, especially children, to drown should they fall through the ice. Despite the risks, skating on the Canal captured the imagination of Ottawa’s citizens who recalled Dutch paintings of skaters on the canals of Holland. If they can do it in the Netherlands, why can’t we do it in frigid Ottawa?
Conditions were perfect for skating during the winter of 1958-59, and attracted thousands onto the ice on the Canal, Dow’s Lake, and even the Ottawa and Rideau Rivers. Owing to public demand, the city’s Parks and Recreation Department asked Ottawa’s Board of Control for $16,000 to maintain a one mile length of canal between Patterson Creek and Bank Street, complete with ramps, changing huts and lightening, for the following winter season. Instead the City coughed up only $2,000, enough for a ramp at Fifth Avenue and a skating lane. It was maintained for just over two weeks from 15 December 1959 to 2 January 1960. Four men and two ploughs mounted on jeeps were unable to keep up with the snow. As well, twenty men using four water pumps were required to keep the ice surface smooth. But as the water was drawn from under the ice, city officials feared that air pockets might form leading to cave-ins. With attendance low, averaging only 30 skaters per day, the experiment was abandoned on 5 January, ending Canal skating for more than a decade.
Despite this setback, people kept the faith. In 1969, the National Capital Commission proposed the establishment of an ice rink on the Canal as a way of “finding imaginative and enjoyable uses for unused resources.” But even as late as December 1970, there were naysayers. In an editorial, the Ottawa Citizen opined that the “durable proposal” of Canal skating was “going nowhere.” Instead, it favoured a temporary outdoor rink with artificial refrigeration be installed by the National Arts Centre across from the Canal.
Douglas Fullerton, the redoubtable chairman of the NCC from 1969 to 1973, would have none of it. On 18 January, 1971, he sent teams of men with shovels to clear a five kilometre stretch of ice, twenty feet wide, from the Arts Centre to the Bronson Street Bridge. It was an instant success; 50,000 Ottawa residents flocked to the canal during the rink’s first weekend to enjoy the experience of skating through the heart of the city. There were glitches, however. During the second year of operations, the shelters provided on the ice for skaters sank. They were subsequently placed on gravel pads. Clearing the snow off the ice and maintaining a smooth ice surface suitable for skating also took considerable on-the-job learning. Within three years, however, NCC crews had improved their technique sufficiently to permit virtually the entire width of the Canal to be cleared for its full 7.8 kilometres length through the city. Changing facilities, bathrooms, skate-sharpening facilities as well as first aid centres were established. Refreshment stands served snacks, hot chocolate, coffee and cider to cold, weary skaters. To facilitate night time skating, lights were added.
In 1979, the NCC inaugurated the first annual Winterlude, or Bal de Niege winter festival featuring winter-related activities as well as snow and ice sculptures. It too was a great success. Naturally, its events centred on the Canal; so much so that Fullerton became concerned that Winterlude might detract from the skating. His fears were misplaced. Winterlude became a major tourist attraction and has attracted thousands of new visitors to the Skateway each winter. Ottawa is now a major winter tourist destination.
For many years, the Rideau Canal Skateway billed itself as the longest natural ice skating rink in the world. However, during the mid-2000s, Winnipeg’s River Trail usurped the title. Measuring 9.32 kilometres in length in 2009, it easily topped the Canal for length. Ottawa residents sniffed that Winnipeg’s Trail, which narrowed in places to no more than a car width was a poor excuse for a rink. Ottawa MP Paul Dewar called it a “cow path” in a tongue-in-cheek exchange with his Winnipeg colleague in the House of Commons. Today, Ottawa’s Skateway claims to be the “largest” outdoor skating rink in the world, equivalent to 90 Olympic-sized hockey rinks, a boast supported by the Guinness Book of Records.
Sources:
Canadian Geographic Travel Club, 2009. “Skating: The Cold War,”.
Capital News Online, 2014. “The history of a record making rink,”
Forks North Portage Corporation, 2014. Red River Mutual Trail,.
New Straits Times,” 1975, “Ice-Skating, The Popular Winter Sports,” 29 June.
National Capital Commission, 2014. “Rideau Canal Skateway,”.
OttawaKiosk.com, 2005. “Fact Sheet-Rideau Canal Skateway,”.
The Age, 1974. “Skate Along Ottawa’s five-mile waterway,” 4 November.
The Citizen, 1984. “Evolution of Ottawa’s Rink,” 7 February.
The Globe, 1874. ”Latest from Ottawa,” 6 March.
The Globe and Mail, 2008. “Only in Canada: Two frozen cities face off over ice,” 8 January.
The Ottawa Citizen, 1960. “Skaters’ Wish Coming True With Rink At Mooney’s Bay,” 20 December.
———————–, 1971. “Canal Open—Night Skating On Its Way,” 24 December.
Image: skating on the Rideau Canada, February 2014 by Nea Powell
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
The Canal Basin: Going, Going, Gone
14 November 1927
Readers may be surprised to learn that the Rideau Canal of the twenty-first century is considerably different from the Rideau Canal of the nineteenth century. In the old days, the Canal was very much a gritty, working canal. While it had its share of pleasure boats that plied its length, commerce was its main function. At its Ottawa end, barges, pulled by horses and men along canal-side tow paths, were drawn to warehouses that stretched from the Plaza at Wellington Street to the Maria Street Bridge (the predecessor of the Laurier Avenue Bridge). Lumber, coal and other materials were piled high along its banks awaiting delivery. Consequently, the Rideau Canal was anything but a scenic port of entry into the nation’s capital. Later, railroads and train sheds replaced the warehouses on the eastern side when the Central Depot, the forerunner of Union Station (currently the Ottawa Conference Centre and soon to be the temporary home of the Senate), opened in 1896. While practical, this was not an aesthetic improvement.
The quality of the Canal’s water during the late nineteenth century was also considerably different than that of today. While we sometimes complain about the turbid nature of the water and the summertime weeds that choke stretches of the waterway and parts of Dow’s Lake, this is nothing compared to the complaints of residents of the 1880s. Then the Canal literally stank. The sewer that drained the southern portion of Wellington Ward, the neighbourhood located between Concession Street (Bronson Avenue) and Bank Street flowed into the Canal at Lewis Street. The smell was particularly bad in spring when the effluent that had entered the Canal through the winter thawed. Reportedly, the stench of festering sewage was overpowering. So bad were the conditions, the federal government forced the municipal authorities to fix things. After considerable delay, a proper sewer was constructed.
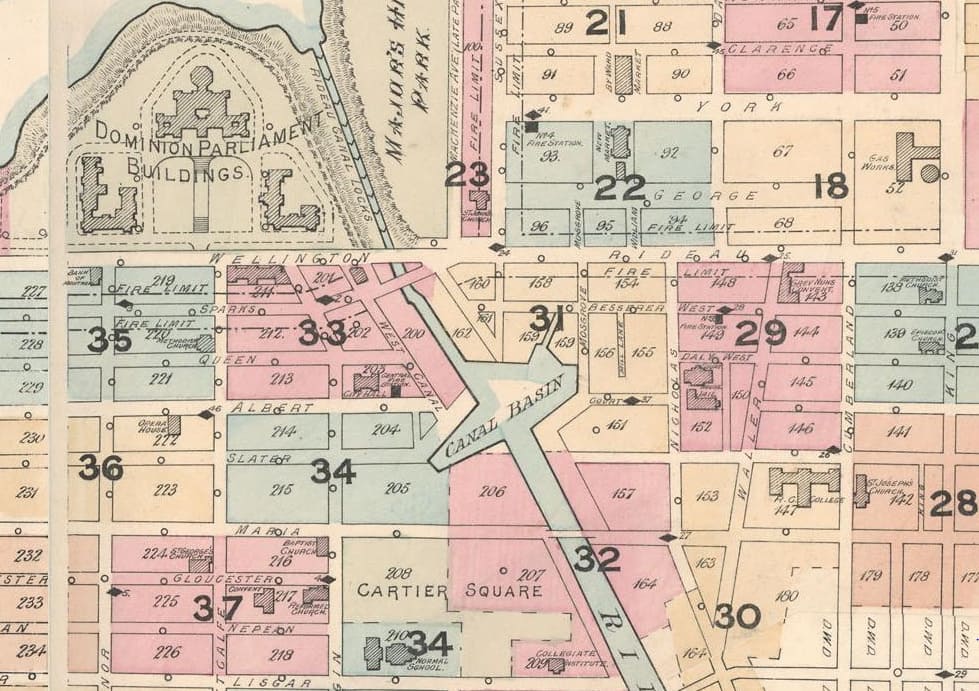 Detail of 1888 Map of Ottawa, City of Ottawa Archives. Note the Canal Basin. By now, only a rump of the By-Wash remained.The other not so delightful feature of the waterway was its flotsam and jetsam. Stray logs—a hazard to navigation—was the least of the problem. Prior to the first annual Central Canada Exhibition held in Ottawa in 1888, one concerned citizen pointed out the many nuisances to be found by boaters on the Canal. These included several carcasses of dead dogs floating in the Deep Cut (that portion of the Canal between Waverely Street and today’s city hall) and a bloated body of a horse bobbing in the water opposite the Exhibition grounds. The citizen also groused about the “vulgar habit” of people swimming in the Canal without “bathing tights.” He didn’t comment on the advisability of canal swimming given the horrific water quality.
Detail of 1888 Map of Ottawa, City of Ottawa Archives. Note the Canal Basin. By now, only a rump of the By-Wash remained.The other not so delightful feature of the waterway was its flotsam and jetsam. Stray logs—a hazard to navigation—was the least of the problem. Prior to the first annual Central Canada Exhibition held in Ottawa in 1888, one concerned citizen pointed out the many nuisances to be found by boaters on the Canal. These included several carcasses of dead dogs floating in the Deep Cut (that portion of the Canal between Waverely Street and today’s city hall) and a bloated body of a horse bobbing in the water opposite the Exhibition grounds. The citizen also groused about the “vulgar habit” of people swimming in the Canal without “bathing tights.” He didn’t comment on the advisability of canal swimming given the horrific water quality.
The physical geography of the Rideau Canal was also different back then. Patterson’s Creek was much longer in the nineteenth century than it is today; its western end became Central Park in the early twentieth century. There was also Neville’s Creek that flowed through today’s Golden Triangle neighbourhood and entered the Canal close to Lewis Street. The Creek, which was described as a cesspool in the 1880s, was filled in during the early twentieth century.
But the biggest difference was the existence of a large canal basin located roughly where the Shaw Centre and National Defence are today on the eastern side of the Canal and the National Arts Centre and Confederation Park are on the western side. This basin, which was lined with wooden docks, was used for mooring boats, turning barges, and picking up and delivering cargo and passengers.
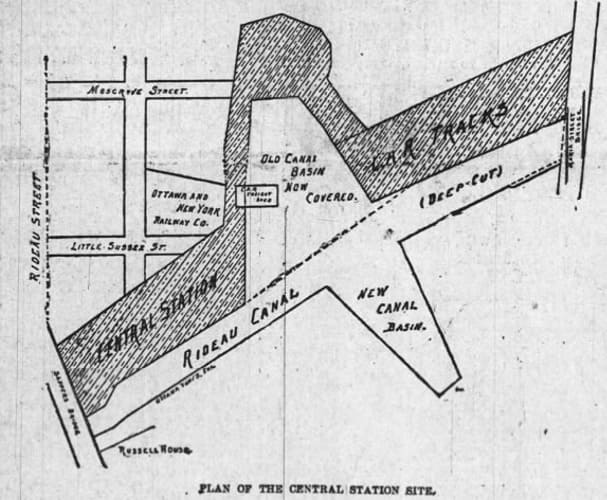 Diagram of the Rideau Canal and the covered eastern Canal Basin, 1897
Diagram of the Rideau Canal and the covered eastern Canal Basin, 1897
The Ottawa Evening Journal, 30 October 1897.Before the Canal was constructed, the canal basin was originally a beaver meadow from which a swamp extended as far west as today’s Bank Street. Following the Canal’s completion in 1832, which included digging out the basin, a small outlet or creek called the By-Wash extended from the north east side of the basin. It was used to drain excess water from the Canal. Controlled by a sluice gate, the By-Wash flowed down Mosgrove Street (now the location of the Rideau Centre), went through a culvert under Rideau Street, re-emerged above ground on the northern portion of Mosgrove Street, before heading down George Street, crossing Dalhousie Street on an angle to York Street, and then running along what is now King Edward Street to the Rideau River. In addition to controlling the Canal’s water level, the By-Wash was used by Lower Town residents for washing and fishing. In 1872, the City successfully petitioned the federal authorities who controlled the Rideau Canal to cover the By-Wash. It was converted into a sewer with only a small rump remaining close to the canal basin that was used as a dry dock.
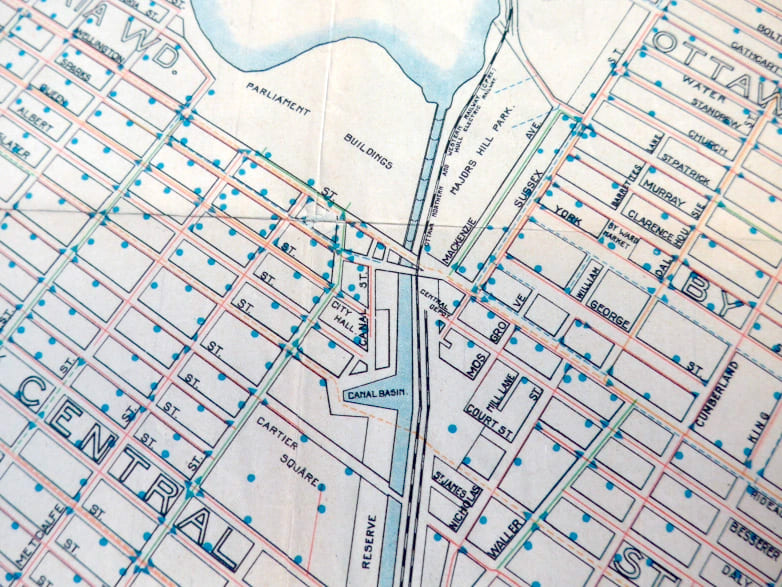 Detail of Map of Ottawa, circa 1900, City of Ottawa Archives. Note that the eastern Canal Basin has disappeared.Big changes to the canal basin started during the last decade of the nineteenth century. John Rudolphus Booth, Ottawa’s lumber baron and owner of three railways, the Ottawa, Arnprior & Parry Sound Railway (the O.A. & P.S.), the Montreal & City of Ottawa Junction Railway, and the Coteau & Province Line Railway & Bridge Company (subsequently merged to form the Canadian Atlantic Railway–CAR), received permission from the Dominion government to bring trains into the heart of Ottawa. Hitherto, his railways provided service to the Bridge Street Station in LeBreton Flats and to the Elgin Street Station, both a fair distance from the city’s centre. In early March 1896, Booth, through his O.A. & P.S. Railway, acquired from the government a twenty-one year lease for the
Detail of Map of Ottawa, circa 1900, City of Ottawa Archives. Note that the eastern Canal Basin has disappeared.Big changes to the canal basin started during the last decade of the nineteenth century. John Rudolphus Booth, Ottawa’s lumber baron and owner of three railways, the Ottawa, Arnprior & Parry Sound Railway (the O.A. & P.S.), the Montreal & City of Ottawa Junction Railway, and the Coteau & Province Line Railway & Bridge Company (subsequently merged to form the Canadian Atlantic Railway–CAR), received permission from the Dominion government to bring trains into the heart of Ottawa. Hitherto, his railways provided service to the Bridge Street Station in LeBreton Flats and to the Elgin Street Station, both a fair distance from the city’s centre. In early March 1896, Booth, through his O.A. & P.S. Railway, acquired from the government a twenty-one year lease for the
east bank of the Rideau Canal from Sapper’s Bridge (roughly the location of today’s Plaza Bridge) to the beginning of the Deep Cut for $1,100 per year “for the purpose of a canal station and approaches thereto.” Lease-holders of properties between Theodore Street (today’s Laurier Avenue East) and the canal basin were told to vacate. After building a temporary Central Depot at the Maria Street Bridge on the Theodore Street side, Booth subsequently extended the line across the canal basin to a new temporary Central Station at the Military Stores building at Sappers’ Bridge.
Initially, the railway crossed the basin on trestles, leaving the basin underneath intact while Booth dredged the western side of the canal basin and built replacement docks—the quid pro quo with the government for removing the eastern basin’s docks. It seems that the government was reluctant to allow Booth to fill in the eastern portion of the basin until the western portion had been deepened, fearing that any unexpected rush of water might be larger than the locks could handle leading to flooding. By mid-March 1896, 75 men and 25-35 horses were hard at work excavating the site. The Central Depot at Sappers’ Bridge was completed in 1896, and was promptly the subject of dispute between Booth and his railway competitors who also wished to use a downtown station. There was rumours that if the Canadian Pacific Railway could not come to terms with Booth, it would build a railroad on the western side of the Canal with a terminus on the other side of Sappers’ Bridge across from the Central Station. Fortunately, with government prodding an accommodation was made. Initially covered over with planks, the western portion of the Canal Basin was subsequently filled in. A new Central Station, later renamed Union Station, opened in 1912.
 Rideau Canal, circa 1911. The western Canal Basin is on the left. Union Station and the Château Laurier are under construction.
Rideau Canal, circa 1911. The western Canal Basin is on the left. Union Station and the Château Laurier are under construction.
Department of Mines and Technical Surveys, Library and Archives Canada, PA-023229.
If the eastern Canal Basin was sacrificed to the railway, the western Canal Basin was the victim of the automobile. This time, the Federal District Commission (FDC), the forerunner of the National Capital Commission, was responsible. Consistent with its plan to beautify the nation’s capital, the FDC in cooperation with the municipal authorities decided to extend the Driveway from the Drill Hall to Connaught Plaza (now Confederation Plaza) at a cost of $150,000. These funds also covered the construction of two connections with Slater Street, a subway at Laurier Avenue, new light standards, landscaping, and a new retaining wall for the Rideau Canal. Again, firms with warehouses at the Canal Basin, including the wholesale grocers L.N. Bate & Sons and the wholesale hardware merchant Thomas Birkett & Son, were forced to relocate. By the end of April 1927, workmen using steam shovels and teams of horses were hard at work filling in the western Canal Basin. Huge piles of earth were piled up near the Laurier Street Bridge ready to be shifted into the basin. On 14 November 1927, the last renovations to the Rideau Canal commenced with the construction of the new retaining wall from Connaught Plaza to the Laurier Street Bridge. With that, the old Canal Basin, which had served Ottawa for almost 100 years, vanished into history.
Sources:
Colin Churcher’s Railway Pages, 2017. The Railways of Ottawa.
Daily Citizen (The), 1895. “Central Station Site,” 1 August.
Evening Citizen (The), 1898. “The New Line.” 11 June.
Evening Journal (The), 1888.” The City Sewerage,” 19 April.
—————————, 1888, “The By-Law,” 27 April.
—————————, 1888. “Canal Nuisances,” 28 May.
—————————, 1895. “Notice to Quit,” 3 October.
—————————, 1895. “Now For The New Basin,” 9 November.
—————————, 1896. “Now For The Depot,” 4 February.
—————————, 1896. “Basin Widening Begun,” 4 March.
—————————, 1896. “Pushing It Ahead,” 11 November.
—————————, 1896. “For The New Station,” 23 May.
—————————, 1897, “Picked From Reporter’s Notes,” 20 October.
————————–, 1897, “Special C.P.R. Depot All Talk,’ 30 October.
————————–, 1898, “The Central Station,” 7 November.
Ottawa Journal (The), 1925. “History of Early Ottawa,” 10 October.
————————–, 1927, “Start Filling Basin Of Rideau Canal,” 26 April.
————————–, 1927. “Artist’s Conception of Park Scheme Proposed by The Prime Minister,” 11 June.
————————–, 1927, “The Railways And he Central Station,” 1 November.
————————–, 1934. “Understanding Shown In Letters Between King Ministry and Ottawa Concerning Beautification of City,” 6 January.
————————–, 1935. “Ottawa’s Beauty Developed On Broad Lines,” 10 December.
————————-, 1949. “Ottawa’s Vanished Water Traffic,” 15 September.
Ottawa, Past & Present, 2014. “Aerial View of the Rideau Canal 1927 and 2014,”.
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
Ottawa’s Chinese Laundry Tax
20 April 1897
Like most countries, Canada has a long, history of racial discrimination and prejudice against minority groups that sadly persists in varying degrees to today. Visible minorities, including Canada’s Indigenous peoples, and immigrants of African and Asian descent, have been particularly targeted as have been religious minorities, such as Jews, Muslims and certain Christian sects, and homosexuals. Chinese immigrants were the subject of draconian laws aimed at curtailing their numbers during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. They only received the right to vote in 1947. Canada’s race-based immigration system remained in force until 1962. Chinese immigrants and Canadians of Chinese descent were also barred from many professions, were forbidden from buying property in certain jurisdictions, and were subject to degrading segregation laws.
The first major wave of Chinese settlers to Canada came from California during the 1850s, attracted by the gold rush in the Fraser Valley of British Columbia. Immediately, they faced discrimination. British Columbia denied Chinese immigrants the right to vote. Later, the federal government did likewise. Another wave of Chinese entered Canada to help build the Canadian Pacific Railway during the 1880s. The Chinese labourers worked for meagre pay in appalling conditions. Many perished. Bowing to pressure from British Columbia, the federal government passed the Chinese Immigration Act in 1885, instituting a $50 poll tax on Chinese immigrant labourers, roughly equivalent to the £10 poll tax imposed on Chinese immigrants in Australia and New Zealand. It was less draconian, however, than the Chinese Exclusion Act than effectively barred Chinese immigration to the United States. The poll tax was a sizeable financial impediment to Chinese immigrants who only earned about $300 per year, and often supported dependents back in China. Most Chinese men who worked on the railways and elsewhere could not afford to bring their wives and families to Canada. This led to broken families and a serious male-female imbalance within the Chinese community. The Imperial government in London, which was at the time in the process of negotiating with the Chinese government over Burma, was not amused. It was, however, reluctant to impose a veto over the Canadian legislation. The Evening Journal thundered in 1886 that “Canada was not interested in Burmah [sic] but she was in the Chinese problem in British Columbia and if the majority of her people desires to shut the Mongolians out, or tax them, it is their own business and nobody else’s.”
Organized labour in Canada was opposed to Chinese immigrants. In Vancouver, the Knights of Labour passed strong resolutions in 1886 against them and organized boycotts of Chinese businesses. A few years later, the Trade and Labour Congress sent a deputation to Sir John A. Macdonald demanding the prohibition of Chinese labour in Canada, saying they were an “undesirable class of immigrants.” The Prime Minister told the delegation that while it was the policy of the government to discourage Chinese immigration, there was no desire to actually prohibit the Chinese from entering the country. Macdonald also rejected a second demand that mines be banned from hiring Chinese workers.
In addition to boycotts, there were nasty anti-Chinese riots in several Western Canadian cities, including Vancouver and Calgary. But, not everybody was opposed to Chinese immigration. Charles Kaulbach, a Conservative member of parliament from Nova Scotia remarked in 1887 that the Chinese “were an essential element in building up the Province of British Columbia.” Despite its earlier remarks, Ottawa’s Evening Journal appears to have had a change of heart in 1887, coming out in support of Chinese merchants who were protesting the $50 poll tax. The newspaper said that the tax was “a political sop to sectional interests,” a “short-sighted folly,” and an “inexcusable injustice.” Subsequently, in response to an anti-Chinese tirade in the Victoria Times, which the Journal claimed was plagiarized from a “slavery paper published before the American [civil] war,” it wrote:
The tendency of English-speaking races to compete with other races by means of clubs has always been interesting. When we want to own negro slaves, or to kill off red men or to boycott Chinese, we cannot only prove ourselves morally right, but woe be to any one who argues with us about it! The rant of the Victoria Times sounds familiar, in fact exceedingly chestnutty.
 Chinese Laundry advertisement
Chinese Laundry advertisement
The Evening Journal, 21 April 1897The first Chinese to come to Ottawa arrived in 1887. In October of that year, the Evening Journal noted that there was a new type of business sign on Spark’s Street—a Chinese laundry called “Wing On.” The following month, the newspaper reported that the city’s Chinese population was growing with the arrival of Chung Kee who was residing on Elgin Street. (In the 1891 census, there were only five Chinese residents of Ottawa, all men, out of a mere 97 in all of Ontario.) The newspaper reported that Chung had established a laundry, the third to have been established by Chinese over the previous six months. Coincidently, the signs of the laundries were all similar. Each used white lettering on a red background. Wing On also made the news the following year when he launched a legal claim against a local company that had supplied the laundry with washing machines. When one broke down after only a week in operation, the supplier refused to honour his warranty. Who won the case is not known. The Wing On laundry went on to become very successful, and by the late 1890s had two subsidiary stores, one on Sussex Street and another on Bank Street, and was a regular advertiser in local newspapers.
In 1888, official Chinese visitors to Ottawa, ran afoul of the $50 poll tax. Three “Celestial” commissioners, Y. l. Foo, H.K. Foo and H.B. Sanamissa, who were appointed by the Imperial Chinese Government to investigate Western agricultural techniques, were stopped at the Canada-U.S. border while on their way to the nation’s capital, presumably to visit the Central Experimental Farm. The three commissioners refused to pay the $50 poll tax. Being government officials, they were supposed to have been exempt from the tax. However, the Canadian immigration officers at the border balked at letting them proceed, and only allowed them to continue their journey under a police escort. Their baggage was impounded as security, and a policeman slept outside their door at the Russell Hotel where they were staying. The Customs Department subsequently backed down, apologized, and returned their luggage.
In 1895, anti-Chinese sentiment in Ottawa began to take on more serious character. The Ottawa Trades and Labour Council passed a motion that all union men should refrain from using Chinese laundries and instead patronize “our own laundries run by white people.” Delegate St. Pierre, who introduced the motion, which was seconded by Delegate Chapman, reportedly said that “The Chinese were driving white people out of British Columbia and they would do the same in Ottawa.” He added that the Chinese were a curse to the city and that the sooner they were driven out the better.”
Two years later, on the 20 April 1897, Ottawa’s City Council voted to impose a $10 per year tax on Chinese laundries. Given the amount of water that laundries were using, the Council’s Waterworks Committee had earlier recommended that Council impose a $10 per year tax on “all Chinese laundries, or small laundries” using city water. However, when the recommendation came to the Board, the measure was limited to just Chinese laundries on an amendment moved by Alderman McGuire, seconded by Alderman Powell. Alderman McGuire, who was the unofficial labour union representative on City Council, said that the measure was a “matter of protection to the interests of our people [italics added] who are striving hard to make a living,” and that Ottawa realized nothing from the Chinese.
Others spoke up in defence of the Chinese. Alderman Campbell said that the Chinese were law-abiding, and always paid their water fees on time. Alderman S. Maynard Rogers thought that if the motion passed, Ottawa would become a laughing stock and didn’t want to act towards Chinese the way they do in the United States. Other councilmen calling the tax “unBritish, “unChristian,” and “unjust.” Nevertheless, the amendment passed on an eleven to six Council vote. The next day, the headline in the Evening Journal read No Pay Taxee; No Washee: Council drops on the Chinese.
Local Chinese residents were rightly appalled. Many gathered at Hong You’s laundry on Bank Street to discuss the tax and decide on what to do. It was agreed that they would find a lawyer and take the City to court on the grounds that Council could not impose a tax on any particular class or nationality. Although this was many years before the rights and freedoms of Canadians were constitutionally protected, the Chinese community had a good case.
At Council, Alderman Campbell tried to overturn the vote. But on two occasions when he raised the issue, supporters of the measure left the Council Chamber and broke the quorum. The issue had to be postponed. Campbell’s amendment, which would have applied the tax to all laundries not just Chinese ones, finally came to vote at the end of May 1897. It was defeated on a twelve to eight vote, thus leaving the discriminatory tax in place. The Evening Journal said that the tax was probably illegal, and seemed “in ill accord with British fair play.”
Behind the scenes, people must have been getting worried about potential law suits and bad publicity. An advisory committee was established to examine the issue that included the Mayor Samuel Bingham and the City’s solicitor M. O’Gara. In late June, the committee issued its report to Council saying that the committee was “of the opinion that the charges for the water rates on laundries should be dealt with irrespective of persons” and directed the waterworks committee to determine “what special rates, if any, should be charged upon premises where laundries are carried on.” The discriminatory tax was never implemented.
Despite this small victory over the forces of discrimination and prejudice, governments continued to pander to sectional interests and the inexcusable injustice inflicted on Chinese immigrants to Canada was to get worse before redress began after World War II. Due to anti-Chinese pressure from British Columbia, the poll tax was increased to $100 in 1900 and then to $500 in 1903 despite there being only 17,312 Chinese settlers in all of Canada at the turn of the 20th century. Things were to go from bad to worse. In 1923, Chinese immigration to Canada was banned under the Chinese Immigration Act also known as the Chinese Exclusion Act. The law remained in force until 1947.
In 2006, Prime Minister Harper issued an apology for the head tax that was enforced from 1885 to 1923 and the exclusionary laws in place from 1923 to 1947. A symbolic payment of $20,000 was also awarded to survivors of the head tax. In 2014, Premier Christy Clark of British Columbia apologized for the more than 160 historical racist and discriminatory policies imposed by the B.C. government on the Chinese. At the end of March 2018, Vancouver Mayor Gregor Robinson announced that the Vancouver City government would apologize for its past discriminatory by-laws and practices.
Sources:
Chan, Arlene. 2017. “Chinese Immigration Act,” The Canadian Encyclopedia.
Chan, Anthony, 2015. “Chinse Canadians,” The Canadian Encyclopedia.
Chong, Denise. 2013. Lives of the Family, Random House Canada: Toronto.
Ottawa City Council. 1897. Minutes, 20 April, 17 May, 30 May, 28 June.
Ottawa Chinese Community Centre and Denise Chong 2012. Lives of the Family.
Evening Journal (Ottawa), 1886. “Editorial,” 3 March.
——————————–, 1886. “The Trades Congress,” 20 September.
——————————–, 1886. “Sparks,” 17 November.
——————————–, 1887. “The Chinese Question,” 19 May.
——————————–, 1887. “Editorial,” 8 September 1887.
——————————–, 1887. “City and Vicinity,” 19 October.
——————————–, 1887. “City and Vicinity,” 23 November.
——————————–, 1888. “On Wing On!,” 3 February.
——————————–, 1888. “Chinamen in Bond,” 22 September.
——————————–, 1889, “The Chinese Tax,” 14 October.
——————————–, 1890. “The Chinese In Canada,” 9 September.
——————————–, 1892. “The Chinese Question,” 28 March.
——————————–, 1892. “Riot in Calgary,” 4 August.
——————————–, 1895. “No Use For The Chinese,” 26 September 1895.
——————————–, 1897. “No Pay Taxee; No Washee,” 21 April.
——————————–, 1897. “Chinamen Indignant,” 3 May.
——————————–, 1897. “Must Be Responsible,” 18 May.
——————————–, 1897. “Editorial,” 2 June.
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
The Arrival of the Iron Horse
25 December 1854
An iconic image of the Industrial Revolution is the train, powering across the countryside, with clouds of smoke and steam billowing from its locomotive’s smokestack. Not only a new, rapid form of communication, the train embodied the scientific and technological discoveries of the age, the heavy industries needed to make and power it, and the innovative manufacturing techniques required to turn out the miles of iron rails on which it ran. Within twenty years of the inauguration of the world’s first steam-powered, interurban rail line between Liverpool and Manchester in 1830, Europe and the Americas were in the grip of a railway mania, similar to the “dot com” bubble of the 1990s. Hundreds of railway companies were formed; many went bust, though not before leaving behind a massive railway infrastructure legacy. The railway transformed the economies of the world, linking distant communities and opening new markets. In the Americas, the railway provided European settlers with access to virgin territory to exploit (and native communities to despoil), and, in the case of Canada, gave birth to a nation that spanned a continent.
The first Canadian railway was constructed in 1836 in Lower Canada, now Quebec. The Champlain and St Lawrence Railroad ran between La Prairie on the St Lawrence to St Jean on the Richelieu River, a navigable waterway that debouches into Lake Champlain. The railway cut hours off the long journey between Montreal and New York City. Railway building began in earnest in Canada following the Guarantee Act of 1849 under which the Province of Canada government offered cheap financing to companies building railways of at least 75 miles in length. Additional government financing was forthcoming after the 1852 Municipal Loan Act. In 1850 there was less than 110 kilometres of railroad laid down in Canada. Ten years later, there was more than 3,200 kilometres.
Discussions to bring the “iron horse” to the Ottawa valley began in 1848. In May of that year, The Packet, the precursor of The Ottawa Citizen, began to enthusiastically promote the building of a railway between Bytown, later to become Ottawa, and Prescott, a small community on the St Lawrence River. Prescott was immediately opposite Ogdensburg, New York which was to be the terminus of a railway linking the St Lawrence River to New York City and Boston. As the only way in or out of Bytown during winter was by sleigh, a rail link from Bytown to Prescott offered the tantalizing possibility of an all-season transportation route for exporting lumber cut from Ottawa valley forests to the important U.S. markets, one that was much speedier and less costly than using the Rideau Canal or the Ottawa River that were locked in ice for four months of the year.
Prescott’s leading citizens held an exploratory meeting with engineers and surveyors in June 1848. A similar meeting took place at the Court House in Bytown the following month. Receiving wide support from both communities, the Bytown and Prescott Railway was incorporated by an act of the Provincial government on 10 May 1850. A prospectus was issued describing the length of the line, its likely location, and its construction and outfitting costs, estimated at £150,000-200,000 (£1=C$4.87). To make it pay, annual revenues of £21,000-30,000 were needed. The possibility of extending the line eastward to link up with the Lachine to Montreal railway was also mooted. The line’s chairman was John McKinnon, the son-in-law of Thomas McKay, whose company helped to build the Rideau Canal, and who was a major lumber mill owner in New Edinburgh, a village he started.
Through the winter of 1850-51, the surveyor, Walter Shanly, with two assistants, mapped out four possible routes from Prescott to Bytown, covering more than 300 miles on snowshoe. On 7 April 1851, Shanly gave his report to the president and directors of the railway company. While stressing the preliminary nature of his survey, he favoured a route to the east of the Rideau River that took the tracks from Prescott through Spencerville, Oxford, Kemptville, Osgoode, Manotick, and Gloucester, before arriving in Bytown. While the terminus at Prescott on the St Lawrence was not controversial, the location of the Bytown terminus was. Some shareholders favoured a spot beside the Rideau Canal Basin (roughly where Confederation Park and the Shaw Centre is located today), while others wanted to build the station on land originally set aside for the military between Nepean Point and the Rideau Falls. The latter option was chosen. It was perhaps not entirely coincidental that the train would conveniently pass in front of Thomas MacKay’s lumber mills. With hindsight, Lebreton Flats, which later was to become the centre of Ottawa’s lumber industry, would have been a much better location, but at the time the area was largely undeveloped.
Funds to build the railway were raised partly by subscription from private shareholders, partly from municipalities, and partly through loans raised in England and Canada. Unfortunately for the railway’s backers, the line, only 52 miles long, was too short to qualify for the provincial subsidy. However, Bytown kicked in £15,000 in equity, and, after the 1852 Municipal Loan Act was passed, provided a massive loan guarantee of £50,000. Tiny Prescott, with a population of only 2,000, provided another £8,000 in capital and £25,000 in loan guarantees. The township of Gloucester chipped in a further £5,000 in equity financing. The links between the towns that provided support, the railway’s largest shareholders, and the railway’s most prominent advocate were unhealthily close, at least by today’s standards. Robert Bell, editor and later owner of the Ottawa Citizen, was the railway’s secretary, as well as a Bytown councilman. John McKinnon, the company’s president, was the reeve of Gloucester.
Workers started to clear land for the railway in early September 1851, with the official ground-breaking ceremony held on 9 October, 1851. A celebratory parade started in front of the railway office on Rideau Street and made its way down Sussex Street. On hand for the big event, were Bytown’s mayor, members of the Town Corporation, the directors and officers of the Bytown and Prescott Railway, a senior magistrate, the area’s member of parliament, the county sheriff, and the “Sons and Cadets of Temperance” in full regalia. That evening, McKinnon and the directors hosted a self-congratulatory dinner at “Doran’s,” a top Bytown hotel. Notwithstanding the presence of temperance followers in the afternoon parade, copious amounts of champagne and wine was consumed, leading to a “number of jovial songs…sung in the course of the evening.”
 Advertisement that appeared in The Ottawa Citizen, 23 December 1854Construction was initially slow but for the most part straightforward; Shanly had done a good job siting the tracks. The most difficult part was crossing a swamp north of Prescott. Here, engineers laid down a wooden causeway as a bed for the train tracks. Once the rails arrived from England from the Ebbw Vale Iron Company in late 1853 and early 1854, the pace of construction picked up. The railway company laid down a narrow 4 ft 8 1/2 in. gauge track, commonly used in the United States and elsewhere, rather than the broad 5 ft 6 in. “provincial” gauge typically used in Canada at that time. The carriages and locomotives were sourced in the United States, with the first locomotive, the “Oxford” delivered by barge in May 1854. Two more, the “St Lawrence and the “Ottawa,” arrived in July. Immediately, the locomotives and carriages were put into service, servicing Kemptville by August, and Gloucester, just three and a half miles from Bytown, by 11 November.
Advertisement that appeared in The Ottawa Citizen, 23 December 1854Construction was initially slow but for the most part straightforward; Shanly had done a good job siting the tracks. The most difficult part was crossing a swamp north of Prescott. Here, engineers laid down a wooden causeway as a bed for the train tracks. Once the rails arrived from England from the Ebbw Vale Iron Company in late 1853 and early 1854, the pace of construction picked up. The railway company laid down a narrow 4 ft 8 1/2 in. gauge track, commonly used in the United States and elsewhere, rather than the broad 5 ft 6 in. “provincial” gauge typically used in Canada at that time. The carriages and locomotives were sourced in the United States, with the first locomotive, the “Oxford” delivered by barge in May 1854. Two more, the “St Lawrence and the “Ottawa,” arrived in July. Immediately, the locomotives and carriages were put into service, servicing Kemptville by August, and Gloucester, just three and a half miles from Bytown, by 11 November.
When the first train arrived in Bytown is a bit controversial. An advertisement placed by the railway in the Ottawa Citizen, dated 14 December 1854, informed its Bytown customers that “trains will start from the Montreal Road near the Rideau Bridge, at the East end of Bytown, at 7 o’clock, A.M. (Railway time).” Simultaneously, the railway discontinued its temporary stage coach service from Bytown to the Gloucester train station. The place of embarkation was just outside Bytown’s city limits. Most authorities place the date of the first train as Christmas Day, 1854, based in part on a later newspaper advertisement which said the train would leave Bytown at 6am, Railway time, staring on 25 December (see above). However, in a speech given eleven years after the event, President Bell of the Railway said the date of the first train was 29 December. Differences in timing may relate to when the Rideau Bridge was finally ready for rail traffic, whether the train carried freight or passengers, or the fog of memory. The official opening of the line occurred on 10 May 1855, exactly five years after the railway company was incorporated. Its name was also changed from the Bytown and Prescott Railway to the Ottawa and Prescott Railway to reflect the city’s new name.
Like many similar ventures of the period, the railway never lived up to the hopes of its shareholders and creditors, and was quickly in financial difficulty. An economic depression in the late 1850s cut into the revenues of the heavily-indebted line. The railway’s Ottawa station was also inconvenient for much of the city’s growing lumber industry located in Lebreton Flats. The building of other rail lines meant more competition and lower prices. At the Ottawa & Prescott’s annual general meeting in May 1863, a faction of shareholders tried to seize control of the failing company; an unseemly brawl ensued. Subsequently, with the railway bankrupt, the company’s senior creditors, most importantly, the Ebbw Vale Iron Company, assumed control. Shareholders and junior creditors, including the municipalities, got nothing. Following a corporate re-organization, the line re-emerged in 1867 as the St Lawrence and Ottawa Railway. In 1881, the Canadian Pacific Railway took over the line, and began using it as a feeder link to its main east-west route. Declining traffic during the 1950s led to the closure of the line, and its rails pulled up. Much of the route was converted into a recreational path. In downtown Ottawa, the Vanier Parkway was constructed where the old Bytown & Prescott Railway used to run. A portion of the old line’s route is still used today by Ottawa’s “O” train.
Sources:
Churcher, Colin, 2005. The First Railway in Ottawa, http://www.railways.incanada.net/Articles/Article2005_1.html.
——————, 2005. First Trips and Early Excursions in the Ottawa Area, http://www.railways.incanada.net/circle/excursions.htm#B&Psod.
Elliot. S. R., 1979. Bytown & Prescott Railway, Bytown Railway Society.
Pilon, Henri, 1972. “Robert Bell (1821-73),” Dictionary of Canadian Biography, http://www.biographi.ca/en/bio/bell_robert_1821_73_10E.html.
The Ottawa Citizen, 1851. “Report, Bytown and Prescott Railway Office, Prescott,” 26 April.
———————-, 1851, “no title,” [official opening of the Bytown and Prescott Railroad], 11 October.
———————-, 1854, “Bytown & Prescott Railway,” 16 December.
———————-, 1854, “Bytown & Prescott Railway,” 23 December.
———————-, 1862. “Railway Celebration,” 23 August.
———————-, 1863, “The Railway Meeting, Disgraceful Scenes!” 22 May.
The Packet, 1848, “The Ogdensburg Railway,” Bytown, 13 May.
————-, 1848. “Proceeding of a Meeting of the Inhabitants of the town of Prescott,” 19 June.
————–, 1848. “Most Important Intelligence – Prescott & Bytown Railroad,” 24 June.
————–, 1848. “Prescott and Bytown Railroad from Prescott Telegraph,” 24 June.
————–, 1848, “Bytown & Prescott Railroad,” 7 July.
————–, 1850. “Prospectus of the Bytown & Prescott Railroad, 30 November.
————–, 1851. “Public Meeting in Gloucester.” 19 April.
————–, 1854, “Bytown & Prescott Railroad, 6 May.
Vanier Now, 2013. The History of the Vanier Parkway-Part One: Bytown and Prescott Railway Company, http://vaniernow.blogspot.ca/2013/02/the-history-of-vanier-parkway-part-one.html.
Images: Churcher, Colin, “All Change at Prescott,” picture of the Ottawa & Prescott Railway’s locomotive “Ottawa,” circa 1861, https://churcher.crcml.org/Articles/Article2008_01.html
Bytown & Prescott Railway Advertisement, The Ottawa Citizen, 23 December 1854.
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
Asphalt Paving Comes to Ottawa
30 July 1895
North American roads in the nineteenth century were bad…very bad. Inter-urban “highways” typically consisted of little more than dirt paths carved through the wilderness. In boggy areas, so-called corduroy roads made of logs placed across the direction of travel were sometimes constructed. (They were called corduroy because their texture was reminiscent of corduroy fabric.) If you were very lucky, your highway might be planked, consisting of four-inch thick wooden planks attached to longitudinal stringers. While relatively comfortable on which to drive, planked highways quickly deteriorated. Regardless of road surface, a journey by stagecoach must have been a slow, jolting and painful experience. Coach passengers were also expected to get out and push if their carriage got mired in mud. Needless to say, few travelled by road unless they had to. The true highways of the age were rivers, canals, and later the railway.
Things weren’t a whole lot better in towns. Urban streets, often made of dirt or gravel, were thick with mud when wet, rutted and dusty when dry, and virtually impassable except by sled in winter. In some well-to-do areas, roads were expensively laid with granite blocks known as sett paving. (This type of paving is sometimes called cobblestone paving, though true cobblestone roads were laid with naturally rounded stones set in mortar.) Another more common road surface in North American cities was cedar block paving, consisting of six-inch logs or squared wood set end down on a gravel base. This type of road was cheap but was subject to wear and rot, and lasted for only a few years before needing to be replaced. Cedar block roads were also extremely slippery when wet.
Relief came in the early nineteenth century with the introduction of roadways made by crushed stone developed by two Scottish engineers, Thomas Telford and John McAdam. Telford roads had a base of large rocks with an upper layer of smaller stones. They were also slightly convex to facilitate drainage. McAdam roads eschewed the expensive rock base recommended by Telford, relying instead on a native soil foundation. The roadway was then built up of stones of graduated sizes, the smallest size on top. Typically, no binding agent other than water was applied. Instead the weight of traffic packed down the stone into a durable roadway. McAdam roads became very popular in Europe and North America through the nineteenth century. (When tar was later added as a binding agent, tarmacadam was invented—“tarmac” for short.)
York Street, from Sussex Street to Dalhousie Street, was the first Ottawa roadway to be “macadamized” in June 1851. Forty years later, the Evening Journal described the capital’s streets as consisting of mostly mud or macadam, with a small amount of stone block paving on Bridge Street in LeBreton Flats and cedar block paving on Wellington Street.
Although macadam roadways were effective, they were also costly to maintain. By one estimate, the annual maintenance cost of a macadam road ran to as much as twenty percent of its original cost. This included daily repairs and patches, frequent sprinkling of water as often as three or four times a day to keep down dust, and the regular use of a heavy roller to pack the road down if traffic was insufficient to do so. Not surprisingly, this was not always done, leading to the deterioration of roadways, and complaints from citizens, especially pedestrians, for better roads.
In the late 1800s, the invention of the modern “safety” bicycle (a safe alternative to the preceding high wheeling, penny-farthing bicycle), led to a biking craze. In cities throughout North America and Europe, men and women adopted this new, invigorating and liberating mode of transportation. Not surprisingly, municipal authorities found themselves under heightened pressure to provide smooth road surfaces.
What cities turned to was asphalt. First used in road construction by the ancient Babylonians in around 600 BC, modern asphalt roads date to about the early 1850s in France. Asphalt roads made their way to the United States roughly twenty years later, and to Canada in the mid-1880s. In 1886, a stretch of St James Street (rue Saint Jacques) in Montreal was laid with asphalt paving using asphalt imported from Trinidad. It was a great success. So much so that traffic on parallel streets diverted to use it. The Journal reported that people preferred the “smoothness of asphalt to the vicious wrenchings of the granite or cedar block pavements.” While far more expensive than other forms of paving, asphalt held the promise of durability with an expected life expectancy of fifteen to twenty years, with much less annual maintenance. Asphalt was also viewed as more hygienic, modern, and aesthetically pleasing. As well, horses and carriages were much quieter on asphalt surfaces, reducing the din of urban life.
In 1889, Mr George Perley and Mr William F. Powell submitted a petition to Ottawa’s city council to have Metcalfe Street from Gloucester Street to Gilmour Street paved in asphalt. Apparently, nine of ten landowners on that stretch of road supported the initiative. However, it never came about as city council baulked at their request that an American contractor be brought in to do the paving without putting the job out to tender.
 Call for Tender of Bids for the Asphalting of Sparks and Bank Streets by the City's Engineer's Office, Ottawa, 7 January 1895, The Evening Journal, 9 February 1895The accolade of being the first asphalted road in Ottawa goes to Sparks Street. This time, a petition of landowners was successful though a vocal minority complained about the cost. In support of conversion, R.J. Devlin, a large retailer on Sparks Street, published a satirical article in the Journal entitled Aye Or No For The Pavement. It read:
Call for Tender of Bids for the Asphalting of Sparks and Bank Streets by the City's Engineer's Office, Ottawa, 7 January 1895, The Evening Journal, 9 February 1895The accolade of being the first asphalted road in Ottawa goes to Sparks Street. This time, a petition of landowners was successful though a vocal minority complained about the cost. In support of conversion, R.J. Devlin, a large retailer on Sparks Street, published a satirical article in the Journal entitled Aye Or No For The Pavement. It read:
No most decidedly! What do we want with a clean, solid and enduring pavement on Sparks street. Haven’t we got on without it in the past? Haven’t we a pretty good street as it is? With the exception of two months in the spring—And six weeks in the fall—And a week now and then every time it rains, Sparks Street is all that could be desired. That is if you wear long boots, Or are handy on stilts. No, gentlemen, we do not want Sparks street paved. What was good enough for our fathers is good enough for us…No, gentlemen, good, plain, everyday mud is good enough for us. It has stuck to us in the past and we will stick to it in the future.
In the end, just over 80% of the landowners by assessed value were in favour, including the Russell House Company, the largest property owner on the block, and W.J. Topley, the noted photographer. The asphalting petition received the City’s Board of Works support and was subsequently approved by City Council in October 1894.
In early 1895, eight bids were received on the contract to pave Sparks and Bank Streets with asphalt. Henry & Smith of Ottawa won with the lowest bid. However, the contract was later cancelled when the company objected to certain terms that the City required. In May 1895, the contract was re-tendered. This time, the Canada Granite Company of Ottawa won with its bid to pave the two streets with rock asphalt from France at a cost of $30,395 and $24,668, respectively. Although another company had provided a slightly lower bid using Trinidad asphalt, the city’s Chief Engineer Robert Surtees rejected it on the grounds that rock asphalt was superior to Trinidad asphalt. (While the original contract called for either grade of asphalt, the second contract specified rock asphalt.) Canada Granite was required to provide a 15-year guarantee, backed up with a blocked deposit worth 30% of the value of the contract. Until the guarantee expired, the company would receive 5 per cent interest from the city on its deposit.
 This grainy photograph by Samuel Jarvis, reproduced from The Evening Journal, 31 March 1951, is the only known image of the laying of the first asphalt on Sparks Street by Mayor Borthwick on 30 July 1895Work on pulling up the old macadam surface of Sparks Street from the corner of Canal Street (now gone but was located roughly where the National Arts Centre is today) to Bank Street began the first week of July 1895 by a team of 60 men and a half a dozen carts. The old stones were re-used to repair the macadam on Somerset Street. The Ottawa Electric Train Company took this opportunity to upgrade its rails on Sparks Street, re-routing its trams onto a temporary track on Wellington Street. Following the laying of a foot-deep foundation, the roadway was ready for paving. On 30 July 1895, Mayor William Borthwick threw onto the road the first shovelful of asphalt at the Sparks and Canal Street corner using a shovel made of polished oak and nickel plate. On one side of the shovel was an engraving of the Parliament Buildings and Ottawa’s City Hall, with a picture of the Granite Company works on the other. There was also a silver inscription that read: “On laying the first asphalt pavement on the streets of Ottawa, junction of Sparks and Canal streets by his Worship William Borthwick, Mayor, July 30, 1895.”
This grainy photograph by Samuel Jarvis, reproduced from The Evening Journal, 31 March 1951, is the only known image of the laying of the first asphalt on Sparks Street by Mayor Borthwick on 30 July 1895Work on pulling up the old macadam surface of Sparks Street from the corner of Canal Street (now gone but was located roughly where the National Arts Centre is today) to Bank Street began the first week of July 1895 by a team of 60 men and a half a dozen carts. The old stones were re-used to repair the macadam on Somerset Street. The Ottawa Electric Train Company took this opportunity to upgrade its rails on Sparks Street, re-routing its trams onto a temporary track on Wellington Street. Following the laying of a foot-deep foundation, the roadway was ready for paving. On 30 July 1895, Mayor William Borthwick threw onto the road the first shovelful of asphalt at the Sparks and Canal Street corner using a shovel made of polished oak and nickel plate. On one side of the shovel was an engraving of the Parliament Buildings and Ottawa’s City Hall, with a picture of the Granite Company works on the other. There was also a silver inscription that read: “On laying the first asphalt pavement on the streets of Ottawa, junction of Sparks and Canal streets by his Worship William Borthwick, Mayor, July 30, 1895.”
The ceremony was followed by the customary congratulatory speeches with the Mayor saying that Ottawa citizens “would enjoy first class city streets.” Mr C. Strubbe, the Montreal agent for La Compagnie Generale des Asphaltes de France, the supplier of the imported asphalt used in the paving, congratulated City Council and said that the paving shows “the progressive spirit of the people of the capital,” and that it marked an “improvement towards the cleanliness and health of the city.” Afterwards, civic and industry officials repaired to the Russell House Hotel for a light luncheon supplied by the contractor.
It took more than three weeks to complete the Sparks Street paving job, far longer than anticipated leading to grumbles from area merchants who were losing money while the street was under construction. In part, the delays were due to an inexperienced work force. While a number of experienced labourers were brought in from Montreal, many of the workers were inexperienced local men. There was also some labour strife. Local workers were paid only $1.40 per day compared to $2.00 per day being paid to the Montrealers. Ottawa workers briefly went on strike for pay equity, but returned to work when they were promised the Montreal wage rate once they were experienced. To help speed up the work, men laboured at night. However, this proved to be counterproductive as the night work was poorly done. One portion of the street had to be redone three times.
It didn’t help that the work was performed under a microscope, with city councillors and regular citizens alike kibitzing all aspects of the paving job, including whether the asphalt being applied was hot enough, whether the scoria stones used to line the tram rails were being installed correctly, and whether there were sufficient drains. The Journal commented that “every free and independent elector and a large number of embryo members of that class of humanity who passed along Sparks street…appointed himself a special committee of one to inspect and test the small patch of asphalt laid,” by poking it with umbrellas, and walking on it to see how it felt and whether they left heel prints in the dark surface.
Sparks street was finally opened for traffic during the third week of August, though the new paving had already been “initiated” by Moses Inkerman who had driven his rag cart over the unfinished roadway just three days after the Mayor had thrown the first shovelful of asphalt. To celebrate the arrival of asphalt paving, the City sponsored bicycle races on Spark Street from Bank Street to the Russell House Hotel during the evening of Monday, 27 August. Thousands of people watched. The festivities didn’t impress everyone, however. The Journal sniffed that “closing such an important public thoroughfare that four young men might disport themselves on bicycles was in some cases much questioned.”
 Detail of February 1903 Plan of the Permanent Roadways of Ottawa, City Engineer's Office, City of Ottawa Archives. Yellow indicates asphalt, blue indicates tar macadam, and grey indicates scoria block. Most of the roads, even Wellington Street in front of the Parliament Buildings, had not yet received a permanent road surface by this date.
Detail of February 1903 Plan of the Permanent Roadways of Ottawa, City Engineer's Office, City of Ottawa Archives. Yellow indicates asphalt, blue indicates tar macadam, and grey indicates scoria block. Most of the roads, even Wellington Street in front of the Parliament Buildings, had not yet received a permanent road surface by this date.
Criticism of the newly asphalted roadway continued. There was a rash of accidents with horses slipping on the new road surface, which was slippery when wet. One horse died after falling in front of the Russell House Hotel. The Journal opined that drivers were being careless and needed to slow down, but also suggested that horses be taught “the asphalt step.” There were also complaints about cleanliness. Unlike porous macadam surfaces, asphalt roads are impermeable. Consequently, horse waste, of which there was a lot, had no place to go. The Journal thought this factor alone would do much to hasten the arrival of motor vehicles. It stated “To have the streets occupied only by silent, rubber-tired carriages and carts, with little mud and no manure will be an extremely pleasant improvement in city life.” The first automobiles arrived on Ottawa streets four years later.
Despite the many complaints, once Sparks Street was completed, work immediately began on asphalting Bank Street. This was quickly followed by Rideau Street. The asphalt era had arrived. Cyclists, and subsequently cars, had the smooth road surfaces that we now take for granted.
Sources:
Bradford, Robert, 2015. Keeping Ontario Moving: The History of Roads and Road building in Ontario, Dundurn: Toronto.
Evening Journal (The), 1887, “Our Future Streets,” 19 March.
—————————, 1887. “Street Paving,” 1 August.
—————————, 1889. “Board of Works,” 29 July.
—————————, 1891. “The Paving Of The Streets,” 21 October.
—————————, 1894. “Asphalt In Sight,” 27 September.
—————————, 1894. “The Battle of the Asphalt,” 2 October.
—————————, 1894. “A Foreman For Each Ward,” 29 November.
—————————, 1895. “Is The Asphalting OK?” 26 July.
—————————, 1895. “They All Tested It.” 31 July.
—————————, 1895. “The Mayor Pleased,” 31 July.
—————————, 1895. “Jottings About Town,” 5 August.
—————————, 1895. “Must go Faster.” 5 August.
—————————, 1895. “Points Of Complaint,” 6 August.
—————————, 1895. “Asphalt Pounders Strike,” 6 August.
—————————, 1898. “The Sparks St. Paving,” 9 August.
—————————, 1895. “Passing Of The Horse,” 22 August.
—————————, 1895. “Bike Races On The Asphalt,” 24 August.
—————————, 1895. “The Town Was Out,” 27 August.
—————————, 1895. “The Asphalt Dust,” 27 August.
—————————, 1895. “On Sparks Street,” 31 August.
—————————, 1895. “Died From A Fall,” 7 November.
—————————, 1951. “First Asphalt On Ottawa Streets,” 31 March.
Haig, Robert, 1975, Ottawa: City of the Big Ears, Haig& Haig Publishing Company: Ottawa.
Longfellow, Rickie, 2015. “Back in Time, Building Roads,” Federal Highway Administration.
Mackintosh, Philip G., 2005. “Asphalt Modernism on the Streets of Toronto, 1890-1900,” Material Cultural Review, Volume 62, Fall.
National Asphalt Pavement Association (NAPA), 2017. “The History of Asphalt,”.
Ottawa, City of, 1894. By-laws 1557, “To Provide for a Local Improvement, Asphalt Roadway on Sparks Street”
Rebel Metropolis.org, 2005. “Cedar Blocks and Devil Strips: Cycling the Streets of 1898,” http://rebelmetropolis.org/cedar-blocks-and-devil-strips-cycling-streets-of-1898/.
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
An Electric Banquet
29 August 1892
During the late nineteenth century, electricity was the cutting-edge, new technology, and Ottawa was Canada’s high-tech capital, thanks to two factors—the entrepreneurial skills of Thomas Ahearn, and the city’s proximity to the Chaudière Falls. In 1887, Ahearn and his partner, Warren Soper started the Chaudière Electric Light and Power Company. The company began producing relatively inexpensive hydroelectricity at the Falls, thereby helping to power Ottawa’s manufacturing sector and lighting Ottawa’s homes and shops with the new-fangled incandescent lights invented by Thomas Edison. The duo also later operated Ottawa’s electrified urban transit system, the Ottawa Electric Street Railway, whose carriages were electrically heated.
 A pictorial description of Thomas Ahearn's electric oven.
A pictorial description of Thomas Ahearn's electric oven.
Canadian Patent Office, 1892In August 1892, the Canadian Patent Office issued three patents to Thomas Ahearn. Sandwiched between his electric water bottle and his electric flat iron, was patent no. 39,916 for an improved electric oven. It was described as “An oven having in its hearth inclosed (sic) pits in which electric heaters are placed.” Just like modern ovens, the interior of Ahearn’s oven was lit by incandescent lamps that allowed a person to monitor whatever was being cooked through a glass window.
While Thomas Ahearn did not invent the first electric oven, there is no doubt that the first dinner entirely cooked using electricity took place in Ottawa on 29 August 1892 at the Windsor House hotel. According to a bemused Ottawa Journal journalist, “a complete repast, comprising a number of courses” was cooked “by the agency of chained lightning.” The hotel proudly proclaimed on its menu that “Every item … has been cooked by the electric heating appliance invented and patented by Mr T. Ahearn of Ahearn & Soper of this city and is the first instance in the history of the world of an entire meal being cooked by electricity.” Even the soup, sauces, and after-dinner coffee and tea were prepared using Ahearn’s electric heaters.
The dinner, or more accurately the feast of some thirty different items, consisted of:
One hundred guests were invited by the hotel’s proprietor, Mr Daniels, to enjoy the banquet. The guest list included Ottawa’s Mayor Olivier Durocher, Warren Soper, as well as the presidents of the Ottawa Electric Railway and the Chaudière Electric Light and Power Companies. Also in attendance were numerous newspaper reporters that ensured widespread publicity. The meal was prepared at the electric tram sheds owned by Ahearn and Soper, and rushed by a special carriage to the hotel located several blocks away. The meal included a twenty-one pound roast of beef, a thirteen pound roast of veal, and three big turkeys that were cooked simultaneously in the cavernous Ahearn oven; apparently, the oven could accommodate twice that amount.
After the meal, which was acclaimed as a huge success, with everything “cooked to perfection,” the guests boarded another special tram and taken to view the oven at the tram sheds. There, Thomas Ahearn, who had stayed back to supervise his oven’s operation, provided an explanatory lecture. The arched brick oven was six feet wide with two Ahearn electric heaters installed in the bottom, powered by electricity generated by the Chaudière Electric Light and Power Company. The “current consumed by the two [heaters] was 43 amperes at 50 volts.” The inside of the oven measured four feet by four feet. Peepholes, covered with heavy plate glass, permitted the chefs to observe the progress of the cooking without having to open the door. A major selling feature was the even cooking of the oven—“no scorching in one part and half-done-ness in another part” said the Evening Journal. As a vote of confidence in the new electric oven, Mr Daniels, the owner of the Windsor House hotel, ordered one of Ahearn’s newly patented ovens to be installed in the hotel’s kitchen.
A few weeks later, there was another, even larger scale, demonstration of Ahearn’s Electric Cooking Oven at the Central Canada Exhibition held in Ottawa. As part of a display of Ahearn electrical products, including electric home heaters, coffee boilers, and special restaurant heaters, a local baker, Mr R.E. Jamieson, used the oven to bake buns, twelve pans at a time, that he sold to the crowds at twenty-five cents each. This was an extraordinary price. A multi-course meal at the Café Parisien on Metcalfe Street could be had for only forty cents. The Electrical Engineer, a New York-based electrical trade journal, quipped that the expression “‘Went off like hot cakes’ now reads in Ottawa ‘went off like electric cakes.’”
The Ahearn oven that the baker used was slightly different from the one used for the Windsor House banquet, having three heating elements instead of two. The extra element was needed to provide additional heat to offset heat loss through the frequent opening of the door in the cooking of multiple rounds of buns. The oven was also equipped with a pyrometer, turn-off switches, interior lights, and a clock. The oven was the hit of the Fair. Thomas Ahearn was awarded a special gold medal for his display of electrical devices.
While Thomas Ahearn and Warren Soper were successful entrepreneurs, making fortunes from their electrically-based, business empire, the Ahearn electric oven proved to be a dud. It was too bulky to be easily used as a household appliance. As well, few homes or businesses were wired for electricity. Even where electricity was available, electric ovens, being energy gluttons, were expensive to operate, and were not initially competitive with the more familiar wood, coal, or gas ovens. It wasn’t until the 1930s that electric ovens became widely accepted.
Sources:
Canadian Patent Office Record and Registrar of Copyrights and Trade Marks, 1893. No, 39,916, Electric Oven, Four Électrique. Vol. 20, Ottawa: Government Printing Bureau.
Daily (The) Citizen, 1892. “Café Parisien,” 8 October.
Electricity, 1893. An Electric Banquet, 14 September, 1892, Volume 3, July 20, 1892 to January 11, 1893.
Electrical (The) Engineer, 1892. Electric Cooking At Ottawa, Can., Volume 14, July-December.
Electrical Review, 1893. A Course Dinner Cooked By Electricity, Volume 21-23, August 27, 1892 to February 18, 1893.
Evening (The) Journal, 1892. “An Electric Banquet,” 30 August.
Innovateus, 2013. Electric Stove.
Library and Archives Canada, 2006. Made in Canada, Patents of Invention and the Story of Canadian Innovation, Thomas Ahearn.
Mayer, Roy. 1997. Inventing Canada: One Hundred Years of Innovation, Vancouver: Raincoast Books.
National Academy of Engineering, 2015. Great Engineering Achievements of the 20th Century.
Images:
Patent No. 39,916, Ahearn Electric Oven, The Canadian Patent Office Record And Registrar of Copyrights and Trade Marks, Vol. 20, Ottawa: Government Printing Bureau, 1893.
Thomas Ahearn’s Oven in Operation, Canada Central Fair, Ottawa, October 1892, The Electrical Engineer, “Electric Cooking at Ottawa, Can.,” Volume 14, July-December, author unknown
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
The Fastest Chicken in the World
16 March 1978
The Americans, the Russians, and now apparently the North Koreans, have their ICBMs, the British their Trident submarines, and the French their force de dissuasion. What does Canada have? We have, or rather had, the chicken cannon. Although fodder for many jokes on the Royal Canadian Air Farce, this piece of Canadian weaponry did more practical good than all the nuclear arsenals of the world. More accurately called the “flight impact simulator,” the chicken cannon, or bird gun, was used at Ottawa’s Macdonald-Cartier Airport from 1968 to 2009 to certify airplane windshields, engines and other aircraft parts against bird strikes.
Collisions with birds represent a serious threat to airplanes, particularly during take-offs and landings when planes traverse avian airspace. (Canada geese have, however, been encountered at 30,000 feet.) A bird striking an airplane in flight has what is known as kinetic energy (E) that is directly proportional to its mass (M) and to the square of its velocity (V). (The formula is E=1/2MV².) Consequently, even a small bird, can do significant damage, including shattering an airplane’s windshield and killing the pilot. Flocks of birds can cause multiple strikes, and if they are sucked into an airplane’s turbines, can lead to catastrophic engine failure.
Birds have collided with airplanes since the dawn of aviation. Particularly problematic are gulls, accounting for roughly half of recorded bird incidents. Orville Wright apparently experienced a bird strike in 1905. Aviation pioneer Cal Rodgers was the first person’s whose death was caused by a bird strike when a gull downed his airplane over the Pacific Ocean near the coast of California in 1912. But research into bird strikes on airplanes didn’t really get going until the early 1950s. In part, this reflected the fact that bird strikes were a fairly rare phenomenon during the early years of flying. Airplanes were small and relatively slow. As well, piston-driven airplane engines are less susceptible to damage from bird strikes that turbine engines with axial-flow compressors such as those used by modern jets and turbo-prop airplanes.
Today, global statistics on bird strikes are hard to come by as many countries don’t collect statistics on plane-bird interactions. Also, many strikes are unreported since they either caused no damage or go unnoticed. However, by one estimate, a bird strike occurs once in every 2,000 flights. Consequently, the odds that any particular flight will experience a bird strike are small. But as there are more than 100,000 aircraft flights every day in the world, this means on average there are at least 50 bird strikes per day. According to the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), there were 13,688 airplane strikes with wildlife in 2014 in the United States, of which almost 97 per cent were represented by birds, with the remainder accounted for by terrestrial animals, bats, and reptiles. (The terrestrial animals and reptiles were hit while the airplanes were taxiing—no flying pigs or pterodactyls. In Australia, there have been kangaroo strikes.) Fortunately, most collisions with wildlife do not lead to human fatalities. FAA statistics show that in the twenty years to end 2013, only twenty-five people died from aircraft collisions with wildlife in the United States, with another 279 injured. In Canada, there have been only two known airplane crashes due to bird strikes that caused human deaths. In 1971, three people died when a Cessna 180 hit a bald eagle in British Columbia. In 1976, a military training jet, a CT-114 Tutor, was also downed by birds near Regina causing the death of its two crewmen.
 Chicken Cannon, Electra Accident 1960. The Eastern Airlines Lockheed Electra aircraft brought down by a flock of starlings, Boston, 4 October 1960
Chicken Cannon, Electra Accident 1960. The Eastern Airlines Lockheed Electra aircraft brought down by a flock of starlings, Boston, 4 October 1960
Aviation Saftey NetworkBesides the loss of life, bird strikes are costly for airlines. Repairing and replacing damaged equipment is estimated to cost as much as US$1.25 billion per year. Added to these direct costs are the costs of prevention, deterrence, and liability paid for by airlines, airline manufacturers, and airports.
Airplane manufacturers began using gas-operated bird cannons to test aircraft windshields during the 1950s. The earliest-known chicken gun was built by de Havilland in England. Canada got into the business during the 1960s following two serious incidents in the United States. In early October 1960, a Lockheed Electra owned by Eastern Airlines struck a flock of starlings shortly after take-off from Boston Logan Airport to Philadelphia. Birds were ingested in three of its four engines causing engine failure and the aircraft to crash. Sixty-two of the seventy-five people on board perished. Two years later, a Vickers Viscount owned by United Airlines en route from Newark, New Jersey to Washington D.C.’s National Airport met a flock of whistling swans flying at 6,000 feet. One or more birds hit the airplane’s left horizontal stabilizer sending the aircraft out of control. All seventeen people on board died.
In light of these accidents, Transport Canada asked the National Research Council (NRC) to establish a committee to look at the problem. A multi-prong approach was taken—prevention, research and testing, certification of aircraft, and bird-proofing. The committee, called the Associate Committee on Bird Hazards to Aircraft, involved Transport Canada, the Department of National Defence, the Canadian Wildlife Service, the major Canadian airlines, aircraft manufacturers, pilots, and NRC aircraft experts.
As part of its research efforts to certify aircraft against bird strikes, the Committee examined a number of methods of “delivering” a bird to its research target before choosing a cannon powered by compressed gas. Alternatives included a steam catapult like those used to launch V1 (Buzz) bombs during World War II, a gunpowder-powered catapult, and a rocket-powered sled on rails. Another (crazy) suggestion was to mount a test cockpit on top of an operational airplane and crash the test cockpit into a live bird that was suspended upside down from a gantry.
 Diagram of the Chicken Cannon
Diagram of the Chicken Cannon
NRCThe chosen design was based on a six-inch bore, British bird gun built in 1961 at the Royal Aeronautical Establishment at Farnborough, England. The NRC’s ten-inch bore gun with a forty-foot long barrel and an overall length of seventy feet was built by Fairly Aviation of Dartmouth, Nova Scotia in 1967. (The longer the barrel the faster a projectile can be fired.) The device had a 60 cubic foot reservoir that was rated to a maximum pressure of 200 pounds per square inch (psi). With the air inside the barrel evacuated, a projectile could be hurled at speeds above Mach 1 (the speed of sound, or 717 miles per hour or 1,195 kilometres per hour).
The projectiles were chickens that had previously been euthanized and frozen. Defrosted before use, they were precisely weighed. Standardized weights of one, two, four and eight-pound birds were used in tests. The bird packages were then loaded into “sabots,” or metal containers with liners whose thickness depends on the weight of the bird being used. A total projectile weight, including sabot and liner, would range from four pounds (1.81Kg) for a one-pound bird to 10.43lb (4.73Kg) for an eight-pound bird. Upon firing, the sabot was captured by an “arrestor” to stop it from hitting the target after the chicken. Synthetic chickens, made of gelatine and fibrous material were used for calibrating the gun. Real chickens, and other fowl, were, however, used in actual tests as there is no substitute for the real, feathered thing. The tests were recorded using high-speed, colour film.
 Aftermath of a test of the Chicken Cannon on an aircraft windshield
Aftermath of a test of the Chicken Cannon on an aircraft windshield
NRCThe bird gun was housed in building U-69 at the Ottawa airport. Initially, the idea was to park an airplane in for certification on a concrete apron in front of the gun. However, with tests typically done on aircraft components rather than on an entire aircraft, a test room was built that allowed year-round operations. The cannon could be moved up and down, while a target could be positioned from left to right. An earthen berm surrounded the test area in case of wayward projectiles. The berm itself was later fenced off to stop cross-country skiers from venturing into the operational zone. The Flight Impact Simulator Facility (FISF) received its certification in September 1968.
The airline industry welcomed the new test facility. Instead of each airline manufacturer building, maintaining, and staffing their own bird guns, which they would only use occasionally, it was more cost effective to go to a dedicated facility. Most major aircraft manufacturers had equipment certified at the NRC’s facility at the Ottawa Airport, including Airbus, Boeing, and Bombardier. To receive certification, a tested part had to be sufficiently durable to a bird strike to permit the aircraft to land safely.
Needless to say, firing dead birds at various pieces of aircraft equipment is a messy business. Feather, guts, and flesh can be distributed widely. There is even a word for this gooey mess—“snarge.” One reason for holding the tests inside a test room is to contain the snarge. There is a story that sometime during the 1960s, the U.S. military conducted a chicken gun test outside in front of invited guests. While the test was successful, the guests, along with their cars in the adjacent parking lot, were splattered with chicken debris.
Most commercial aircraft certification tests are performed at under 40 psi, simulating aircraft speeds of up to 350 miles per hour—likely speeds at which aircraft might encounter birds on take-offs and landings. However, tests were also performed on military aircraft that fly at considerable higher speeds. As well, military jets often travel close to the ground where they are more likely than commercial craft to come into contact with birds. On 16 March 1978, the NRC’s 10-inch bore bird cannon fired a 1 kilogram (2.2 pound) chicken projectile at a speed of Mach 1.36, equivalent to 1,040 miles per hour or 1,674 kilometres per hour—as fast as a 7.62mm round of ammunition. This made it the fastest chicken in the world.
Along with the 10-inch bore gun, the FISF had a second, smaller 3.5-inch bore gun used for testing the impact of small birds, hail, 20mm cannon slugs, and other small flying objects. It was even used to test atomic pacemaker battery casings. A five-inch gun was later built in Ottawa to perform tests on the ingestion by engines of birds and ice shed off of the wings and fuselage of airplanes. It was subsequently dismantled. In addition to testing the durability of parts of both fixed-wing and rotary-wing aircraft, as well as the ingestion of birds by engines, the chicken cannons were also used in high impact tests of the durability of aircraft “black boxes”—the now orange-coloured flight data and cockpit voice recorders.
Over the career of the Flight Impact Simulator Facility more than 3,500 shots were fired, using roughly 3.5 tons of chickens. After long, honourable careers, both the 10 inch and 3.5 inch chicken cannons were retired in 2009. In 2012, the guns were donated to the Canada Aviation and Space Museum.
Despite precautionary efforts at airports to reduce the risk of birds colliding with aircraft during take-offs and landings, including making the airfields less desirable to birds, bird strikes continue to occur. In January 2009, US Airways, flight 1549, an Airbus A320, was famously struck by a flock of Canadian geese at an altitude of close to 3,000 feet on takeoff from New York’s LaGuardia Airport. With both engines stalling, the pilot ditched into the Hudson River. Dubbed the “Miracle on the Hudson,” all passengers and crew were safely rescued. In April, 2016, a Dallas-bound, American Airlines Airbus 321 jet was struck by a bird thirty minutes after takeoff from Seattle, severely denting its nose cone. The pilot safely returned the airplane to Seattle with more than 150 persons on board.
Such occurrences underscore the importance of continued research into deterrence and protection of aircraft from flying objects, including the latest threat in the skies—drones. Canada remains a leader in the field through work conducted by the Bird Strike Association Canada and its Bird Strike Committee which is endorsed by Transport Canada, and is organized according to guidelines issued by the International Civil Aviation Association. Canada is also a member of the World Bird Strike Association that meets regularly to share research and ideas.
Sources:
Many thanks to Ron Gould who, along with Ron Elmer, told me the story of Canada’s bird gun and the Flight Impact Simulator Facility. Ron Gould was the Technical Officer at the National Research Council who operated the bird guns from 1976 to his retirement in 2010.
ABC News, 2016. American Airlines Aircraft Returns to Seattle Airport After Damaging Bird Strike, 27 April.
Aviation Safety Network, 2017. “Lockheed -188A Electra, Eastern Airlines, 4 October 1960,”.
Aviation Stack Exchange, 2017. “How many bird strikes are there per year? Any world-wide statistics?.
——————————. 2017. “Vickers 745D Viscount, United Airlines, 23 November 1962,” .
Bird Strike Association of Canada, 2017.
Gould, R. W., 2007. “Really Big Guns, The Origins of Compressed Air Cannons and their use at the NRC,” National Research Council of Canada.
Fortier, R. 2012. “Acquisition Proposal, Items linked to bird strike research by the NRC,” Canada Aviation and Space Museum.
McKinnon, Bruce and Searing G, 2016. “History of Bird Strike Committee Canada,” Bird Strike Association of Canada,.
National Research Council, 2007. “It’s a Bird, it’s a Plane … It’s a Bird Striking a Plane,” 7 January.
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
Britannia-on-the-Bay
24 May 1900
During the late nineteenth century, electricity was the big new invention that was transforming peoples’ lives. Within a short span of years, electric lights replaced gas lamps in homes, in businesses and on city streets in the major cities of North America. Horse-drawn public transportation was also retired in favour of electric streetcars, also known as trolleys. But while the fast and comfortable trolleys were very popular on weekdays and on Saturday mornings transporting commuters from the suburbs to downtown offices, streetcar companies found their vehicles underused on Saturday afternoons and Sundays. What to do? The answer was to increase weekend ridership by giving people someplace to go and something to do on their time off. Spurred by the success of Coney Island in New York City, transit companies in many major North American cities built amusement parks, colloquially known as “electric parks.” Constructed at the end of a streetcar line, these parks attracted thousands of working class men, women and children seeking weekend fun and excitement. Of course, people had to buy a streetcar ticket to get there; the days of the automobile were still in the future.
Ottawa-Hull was no exception to these trends. Thomas Ahearn and Warren Soper introduced the electric streetcar to the nation’s capital in 1891. Four years later, their Ottawa Electric Railway Company (OERC) opened the West End Park on Holland Avenue in Hintonburg, which was then on the outskirts of the city. Later known as Victoria Park, following the Diamond Jubilee of Queen Victoria in 1897, the park was the home to many rides and musical entertainments. The West End Park was the location of the showing of the first motion pictures in Ottawa in 1896. Across the Ottawa River two miles west of Aylmer, the Hull-Aylmer Electric Railway Company opened “Queen’s Park,” in May 1897, again named in honour of Queen Victoria, at the western terminus of its line. Among the attractions at this park, located on Lac Deschênes (a widening in the Ottawa River rather than an actual lake), were a merry-go-round, a water chute and a “mystic maze.”
To compete with the Queen’s Park development in Quebec, the OERC acquired eighteen acres of land in the little summer cottage community of Britannia Village to the west of Ottawa. There, it established in 1900 an amusement park, with swimming and boating facilities on the Ontario side of Lac Deschênes, with a purpose-built tramline linking the new park to downtown Ottawa. Appropriately, it was called the Britannia line. Thomas Ahearn gave journalists a sneak preview of the new line in mid-January 1900. Although the rails had been laid all the way to Britannia Village, at that date the electric lines only went as far as Richmond Road. But the tramline was completed in time for its official opening at 6am on the Queen’s Birthday holiday on 24 May 1900. From the post office at the corner of Sparks and Elgin Streets to Britannia-on-the-Bay tram stop took just twenty-eight minutes, much of which was through the city. The trip from Holland Avenue, the previous end of the line, to Britannia-on-the Bay, with stops at Westboro, Barry’s Wharf and Baker’s Bush, took only eight minutes. The cost for the trip from downtown was initially set at 10 cents—the usual 5 cent fare plus another five cents to travel on the newly completed Britannia line. The five-cent supplement was later dropped.
In and of itself, the trip to Britannia-on-the-Bay was an exciting adventure for Ottawa citizens at the dawn of the twentieth century. Carried in specially-made carriages, trolley goers were taken along rails that ran close to the south side of Richmond Road except for the last mile or so where they crossed Richmond Road to head into Britannia. After leaving the city, which essentially ended at Preston Street, people journeyed through fields of grain and cow pastures, past fine homes and shoreline cottages before reaching their destination. A journalist on the initial January test run said there was a number of long grades with several sharp turns that give the route “a rolling appearance” which will “add zest,” since “pleasure-seeking humanity likes a spice of danger with its bit of fun.” He added that between Hintonburg and Britannia, there were a number of lovely spots.
 The footbridge over the CPR tracks at Britannia Park, 1900
The footbridge over the CPR tracks at Britannia Park, 1900
Henry Joseph Woodside, Library & Archives Canada, PA-016975On reaching Britannia-on-the-Bay, riders crossed to the park, its beach and a long pier via a high footbridge, built at a cost of $1,500 by the OERC, which went over the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) tracks that ran north of the tramline. The footbridge allowed visitors to the park to avoid any danger of being hit by passing trains. On the other side were picnic gardens, concession stands as well as bathing and boating facilities on a thirty-foot wide pier that extended 1,050 feet into Lac Deschênes. The pier was built of wood with a stone base, using material excavated by the Metropolitan Power Company in an earlier failed attempt to build a canal and hydroelectric generating station at Britannia. Lit by electric lights at night, the pier was furnished with seating that ran along its length, perfect for visitors to sit and enjoy the sights, listen to band concerts, and to watch the promenading crowds. At the end of the pier was a perpendicular, two hundred foot long breakwater that protected moorings for boats. At the land end, two octagonal pavilions were erected at a cost of $2,500, housing a restaurant, changing rooms and bathrooms, a ladies’ parlour and sitting rooms.
The weather on opening day was bright and fine, attracting thousands of Ottawa picnickers to try out the OERC’s new park and pier at Britannia. Although the pavilions were not quite completed, they “were temporarily fitted up for use” for the estimated crowd of 12,000-15,000 visitors. The band of the 43rd Battalion gave a concert in the afternoon and evening to the multitudes. When darkness fell, the park was brilliantly illuminated by electric lights. Ten large arc lights lit up the pier.
 Britannia Pier, 1900
Britannia Pier, 1900
Henry Joseph Woodside, Library and Archives Canada, PA-016976The new Britannia Park was a big success, and over the next several years was considerably improved and expanded. With the new waterside park eclipsing the old Victoria Park on Holland Avenue, the OERC cannibalized the latter’s attractions, moving its merry-go-round and auditorium to Britannia. In 1904, the OERC increased the size of the park by buying the 35-acre Mosgrove property close to Carling Avenue. It also extended the pier by four hundred feet, at the end of which a three-story boat house was erected that became the Britannia Boating Club’s clubhouse. In addition to rooms for members and a lower storage area for boats and canoes, which were available for rent by visitors, the clubhouse had a large ballroom and grandstand for spectators. At night, a searchlight on top of the building played over the darkened waters of Lac Deschênes. Other attractions at Britannia Park included excursions on the double-decker, side-wheeler, steamer G.B. Greene, the “Queen” of the Ottawa River which took tourists upstream to Chats Falls two or three times a week. Through the summer, holidaymakers were entertained by the festivities and music of “Venetian Nights.”
 Britannia Boating Club, c. 1907
Britannia Boating Club, c. 1907
William James Topley, Library and Archives Canada, PA-009028Britannia Park enjoyed its peak of popularity before World War I. Then things started to sour. In 1916, the G.B. Greene burnt. Though it was rebuilt, with Canada at war sightseeing wasn’t as popular as in the past. The steamer ended up towing logs and was dismantled in 1946. In August 1918, the Clubhouse at the end of the pier was consumed by flames. Some two hundred canoes and boats, along with the personal effects of members as well as trophies, furnishings and other valuables were lost. Although the cause of the $50,000 fire was never accurately determined, it was believed that a lighted cigarette carelessly thrown into the window of a bathroom was to blame.
Through the 1920s, amusement parks everywhere began to lose their allure. With more and more families owning their own automobile, people had the luxury of exploring other entertainment options. No longer were they limited to where the trolley could take them. Queen’s Park outside of Aylmer closed. Britannia limped on. The Park’s Lakeside Gardens Pavilion still managed to pull in the crowds for dances through the 1930s. Sunday band concerts also remained popular. In the early 1930s, the OERC began promoting the Park as a great place for parents to send their children. For youngsters under 51 inches tall, (i.e. roughly 8 years old or less) the trolley company advertised that they could travel to Britannia for only 6 4/7 cents, total fare, if they purchased a book of seven tickets for 25 cents plus an additional 3 cent fare for the Britannia line. Under its policy of “Safety First,” the trolley company said that special attention and care would be given to children by its car men. “It is therefore possible to send children to Britannia-on-the-Bay with the assurance that they will be safe while going, while at the beach and while returning.” Clearly this was a different time with a different level of care expected of parents. Few today would consider sending young children to swim at a public beach on city transit without formal supervision.
By the late 1940s, Britannia Park and Britannia beach were becoming shabby from years of use and limited maintenance. Transit consultants advised the financially weak OERC to close the park. In 1948, the Ottawa Transport Commission, which was owned by the City of Ottawa, took over the transit company, including its Britannia property. Concerned that the park was continuing to deteriorate, the City decided in 1951 to operate it directly. Some improvements were made, including the building of a children’s miniature railway at the park. However, more grandiose plans that include a zoo, stock-car racing and two artificial pools never left the drawing board. Park infrastructure continued to rot. Meanwhile, the beach was becoming fouled by weeds and pollution. By 1954, what had been one of Canada’s top tourist attractions was now considered “Canada’s worst.” That year, the footbridge over the CPR tracks was demolished. (The trains themselves continued to go through the Park until they were re-located out of downtown Ottawa in 1966.) In 1955, the aging Lakeside Gardens burnt to the ground.
 Defunct Trolley Station Britannia Park, 2015
Defunct Trolley Station Britannia Park, 2015
Photo by James Powell
New investments were finally made into the park in 1958. The rotting wooden pier, now deemed unsafe, was demolished. The stone base of the original 1,050 foot pier built in 1900 was widened and the beach expanded. Lakeside Gardens was also rebuilt for dances. With these changes, the Park experienced a brief renaissance. However, it was not to last, doomed by changing tastes, and for Lakeside Gardens, the lack of a liquor licence. The beach was also increasingly shunned owing to a persistent weed problem. City efforts to control the weeds using bulldozers, chemicals and tons of rock salt proved fruitless. (This was a time before much consideration was given to the environment.) In any event, pollution closed the beach for extended periods. During the 1960s and 1970s, Britannia Park was threatened by a planned extension of the Ottawa River Parkway (today’s Sir John A. Macdonald Parkway) through the Park using the old CPR right-of-way, now turned into a bike path, as well as the construction of the Deschênes Bridge that would have link Aylmer to Ottawa. Both ideas were finally scuppered by opposition from area residents and changing government priorities.
Today, Britannia Village, annexed by Ottawa in 1950, is no longer a remote summer cottage community. Businesses and housing have long filled the open space between the old City of Ottawa and Britannia and beyond. The streetcars that once linked it to downtown are gone; the last trolley to Britannia-on-the-Bay rode into history in 1959. But the magnificent park and beach endure. Owing to the marked improvement to the water quality of the Ottawa River due to the closure of the pulp and paper mills that had polluted it with their effluent, and the treatment of sewage by riverine communities, boaters and swimmers have returned. While Britannia Park and its beach may no longer attract the hordes of day trippers they did every weekend one hundred years ago, they remain a popular summer destination for people trying to escape the heat of the City. The Ron Kolbus-Lakeside Centre, formerly the Lakeside Gardens, also continues to host big band dances as well as education courses ranging from the arts and crafts and dog obedience, to yoga and fitness.
Sources:
Evening Journal, (The), 1897. “Handled The Motor,” 27 May.
—————————-, 1900. “The New Electric Line To Britannia,” 15 January.
—————————-, 1900. “Searchlight on Lake Deschenes,” 2 April.
—————————, 1900. “Ottawans Loyally Observed the 24th,” 25 May.
—————————, 1906. “A Good Show At Britannia,” 22 May.
—————————, 1918. “Britannia Club House Is Destroyed By Fire Loss Nearly $50,000,” 30 August.
—————————, 1931. “The Children’s Beach At Britannia-on-the-Bay.” 13 July.
—————————, 1948, “Battle Of Seaweed Goes On At Britannia,” 1 May.
—————————, 1951. “Britannia Park Is Saved,” 21 June.
—————————, 1954. “Recommend Closing Britannia Park Amusement Centre,” 27 May.
—————————, 1954. “State of Britannia Park,” 28 May.
—————————, 1954, “At Last New Deal Coming For Battered Britannia Park,” 23 July.
Ottawa, (City of), 2016. Ron Kolbus-Lakeside Centre.
Taylor, Eva & Kennedy, James, 1983. Ottawa’s Britannia, Britannia Historical Association, Ottawa.
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
The Soviet Embassy Fire
1 January 1956
It was Sunday, 1 January 1956. Like most New Year’s Days, revellers from the previous night’s festivities were nursing sore heads. With Monday being a holiday, many Ottawa residents were happy to laze about the house and enjoy their long weekend. The virtuous and hardy braved sub-zero Fahrenheit temperatures to go to church, or attend the annual Governor General’s New Year Levee. Held on Parliament Hill, more than 1,000 Ottawa residents filed into the crimson and gold Senate chamber late that morning to be greeted by Governor General Vincent Massey, before receiving a glass of punch and a light lunch in the nearby Railway Committee Room. As was customary at the time, it was a very masculine affair. Other than Charlotte Whitton, Ottawa’s formidable mayor, and some female members of the armed forces, there were very few women present. The city’s diplomatic corps was well represented, however. Among the foreign dignitaries at the reception to shake Massey’s hand were three uniformed representatives of the Soviet Embassy. Little did they realize they were about to have a very bad day.
Following the levee, which ended in the early afternoon, the three Russian officers undoubtedly hurried back to the Soviet embassy for their own New Year’s celebrations, hosted by Ambassador Dimitri Chuvahin. Located at 285 Charlotte Street in Sandy Hill, the embassy building had once been the mansion of the Booth family, Ottawa’s lumber barons. Requisitioned by the Canadian government in 1942 for use by the Royal Canadian Women’s Naval Services, the house was instead turned over to the Russians to house the growing Soviet legation. As guests left the Soviet reception at about 4.15pm, Miss Diane Destonis, a neighbour living in the apartment building across the street, spotted smoke drifting from a window on the third floor of the embassy building. Another neighbour, Mr W. Dore, also saw the smoke. Believing it was a kitchen fire, he tried to alert the Soviet embassy by telephone; he received no reply.
The fire was caused by an electrical short circuit in the embassy’s communications room located on the upper floor of the three-storey building. Instead of immediately calling the Ottawa Fire Department for assistance, Soviet diplomats tried to put out the blaze themselves using hand extinguishers and a small fire hose installed in the building. Thirty minutes passed before the alarm was raised. Although firefighters were on the scene within ten minutes of receiving the call, flames had already engulfed the third floor. Entering by the front door of the embassy, Ottawa’s firemen, led by Chief John Foote, were stopped by embassy staff claiming diplomatic immunity. A Soviet official actually struck Chief Foote; the incident was later played down. Denied access to source of the fire, the firemen were obliged to tackle the blaze from the outside. The Soviet diplomats also impeded the firemen’s efforts by refusing to vacate the premises. Instead, they repeatedly went in and out of the embassy to retrieve filing cabinets, boxes, and files of documents. The last item to be saved from the flames was “a heavy piece of wireless equipment.” Two embassy cars, stuffed with documents, reportedly “careened” out of the embassy driveway onto Charlotte Street, running over deployed fire hoses, almost bursting them.
Incensed by the lack of Soviet co-operation, Chief Foote contacted Mayor Whitton who hurried to the scene. Shortly afterwards, R. M. Macdonnell, the deputy undersecretary of External Affairs arrived, as did Paul Martin, Sr, Minister for National Health and Welfare, substituting for Lester Pearson, Minister for External Affairs who was out of town. The mayor authorized Chief Foote to exercise all necessary emergencies powers at his disposal as Fire Marshall. At 6.30pm, he declared a state of emergency, calling in extra firemen and police support.
The fire was finally brought under control two hours later, but was not extinguished until close to midnight. One hundred firemen fought the blaze in biting cold weather, using equipment from four stations, including three pumper trucks and four ladder trucks. Although smoke and hot cinders filled the sky, a north-easterly breeze blew burning embers towards parkland and the Rideau River, sparing the embassy’s neighbours. More than three thousand spectators watched the night’s drama despite the cold. Hundreds of cars lined Riverside Drive. Meanwhile, streetcar service along Laurier Avenue East was blocked.
Thankfully, no lives were lost in the fire. But the embassy building was a write-off. Estimated losses amounted to $250,000 (equivalent to more than $2 million today). Ambassador Chuvahin and his wife, along with two other Soviet diplomats living in the building, lost their homes and their belongings. The Soviets set up a temporary embassy a short walk away at 24 Blackburn Avenue, the office of the Soviet commercial counsellor.
The next day, with the embassy building sheathed in ice, the blame game commenced. The Soviets claimed that the Ottawa Fire Department had been slow to respond, and that there had been insufficient water pressure. Mayor Whitton hotly denied the allegations, saying that the Russians had only themselves to blame by not calling in the firemen immediately, and then obstructing their access to the building. She also argued that the six-foot, spiked, iron fence installed around the perimeter of the property the previous year had made it difficult for fire equipment to be brought close to the embassy building. Additionally, extreme cold temperatures meant that water being directed onto the blaze vapourized before contact. At the city’s official New Year Reception held that afternoon, a hoarse and weary Mayor Whitton commented, “I’ve been fighting the Russians.”
The public was baffled by the Soviet effort to obstruct Ottawa’s firemen. A Citizen editorial called it “an incomprehensible act,” which put its neighbours at risk. Claims of “diplomatic immunity” in such circumstances were deemed “fantastic.” Igor Gouzenko, the Soviet cypher clerk who had defected from the Soviet Embassy nine years earlier, explained that the only reason for embassy officials to impede and delay Ottawa’s firemen was to ensure that it’s most secret documents, for example, lists of names of agents in the west and instructions from Moscow, were kept secret.
Mayor Whitton called upon the federal government to review its regulations governing diplomatic immunity in order to give firemen free access to buildings in the event of future fires. The government demurred, arguing that international rules governing diplomatic immunity had been finely crafted over many centuries, and that Canadian officials abroad were accorded the same privileges as foreign representatives were in Canada. When contacted, other diplomatic missions in Canada were also wary of any change to the law, though several commented that they would have allowed the firemen onto their premises had their embassies caught fire.
 With the old Booth mansion a write-off, a new Soviet Embassy, built in the Socialist Classical style, was constructed on the same site. With the Cold War in full swing, RCMP counter-espionage agents, assisted by British MI5 agents, apparently concealed microphones in the windows of the new building while it was under construction. Called Operation Dew Worm, Igor Gouzenko provided advice to the Canadian and British spooks on the best locations to place the bugs.
With the old Booth mansion a write-off, a new Soviet Embassy, built in the Socialist Classical style, was constructed on the same site. With the Cold War in full swing, RCMP counter-espionage agents, assisted by British MI5 agents, apparently concealed microphones in the windows of the new building while it was under construction. Called Operation Dew Worm, Igor Gouzenko provided advice to the Canadian and British spooks on the best locations to place the bugs.
It seems, however, that western spy agencies gained little by this piece of high-tech skullduggery. Two books published in the 1980s, Their Trade is Treachery (1981) by journalist H. Chapman Pincher and Spycatcher (1987) by former MI5 agent Peter Wright, claim that the Russians were tipped off to the location of the bugs, and established a secure room elsewhere in the building. Allegedly, the source of the tip-off was a senior member of the British intelligence service, possibly Sir Roger Hollis, director-general of MI5 from 1956 to 1965, whom the authors claim was a Russian mole. The British government officially denied the allegations. But Wright’s memoir gained world-wide notoriety when the British government tried to keep it from being published. The case against Hollis, now dead (as are Pincher and Wright), remains unproven. The Soviet Embassy building now houses the Embassy of the Russian Federation.
As a postscript to this story, history repeated itself in January 1987. When a small, electrical fire broke out in the basement of the Soviet consulate on Avenue de Musée in Montreal, Soviet diplomats choose to fight the blaze themselves using garden hoses and snow. When neighbours called in the alarm to the fire department, Soviet officials delayed the firefighters’ entry into the building for fifteen minutes to protect documents. As a consequence, what had been a minor fire became a major five-alarm fire.
Sources:
City of Ottawa, 2014. “Soviet embassy fire,”
Gouzenko, Igor, 1956. “Secret Work of Russian Embassy Vastly Expanded Since Spy Trials,” The Ottawa Citizen, 4 January.
Lewiston Daily Sun, 1956. “Soviet Ottawa Embassy Destroyed By Fire; Aides Stay To Move Documents,” 2 January.
Los Angeles Times, 1987. “Soviets Keep Firemen Out, Montreal Consulate Burns,” 17 January.
The Globe and Mail, 1956. “Report Chief Struck—Embassy in Ottawa Burned As Russians Impede Firemen,” 2 January.
————————, 1956. “1000 Call on Massey at Levee,” 3 January 1956.
————————, 1981, “The Spy Scandal: Did Canada bug rebuilt Soviet Embassy?,” 27 March.
Toronto Star, 1987. “Fire at Soviet embassy revives 31-year puzzle,” 18 January.
The Ottawa Citizen, 1956. “Mayor Asks Way To Pry Open Embassies During Emergencies,” 3 January.
———————-, 1956. “Weary, Semi-Ill Mayor Entertains At Reception,” 3 January.
———————, 1956. “No ‘Immunity’ From Fire,” 3 January.
———————, 1956. “Flames Ruin Embassy, Red Tape Slows Fight,” 3 January.
———————, 1956. “Refused to Leave, Carried from Burning Building,” 3 January.
———————, 1956. “Senator Feared For Safety of Next-Door Residence,” 3 January.
———————, 1956. “Ottawa’s Diplomats Decidedly Cool Toward Any Curtailment of Privilege,” 4 January.
———————, 1956. “Traditional Colorful Scenes At Governor-General’s Levee,” 3 January.
Wright, Peter, 1987, Spycatcher: The Candid Autobiography of a Senior Intelligence Officer, Stoddart Publishing Co. Ltd: Toronto.
Images:
Soviet Embassy after the Fire, 1956, City of Ottawa, 2014. “Soviet embassy fire,”
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.
Armistice Day
11 November 1918
The headline in The Citizen said it all: “PEACE! World War Ends; Armistice Signed; Kaiser Is Out; Revolution Grows.” After four years and a half years of fighting, the war was over. Shortly after 5am, Paris time, on 11 November 1918, the German politician Mathias Ezberger signed the armistice on behalf of Germany in a railway carriage in the forest of Compiègne, about 60 kilometres north of Paris. It was to take effect six hours later, allowing time for the news to reach the front—a delay that cost many men their lives as fighting continued right up until 11am. The last Canadian soldier to die in the war was Private George Lawrence Price of the 2nd Canadian Division who was killed at 10.58am by a sniper while his unit attempted to take the small Belgian village of Havré near Mons.
News of the armistice reached Ottawa via an Associated Press dispatch at 3.06am that Monday morning. Seconds later, electric lights throughout the capital blinked four times—a pre-arranged signal organized by The Ottawa Citizen with the Ottawa Electric and Hydro-Electric Companies to indicate the arrival of peace. Except for patrons of all-night diners, most Ottawa citizens were home in bed, though many had left their lights on in hopes of witnessing history in the making.
Two days earlier, mid-Saturday afternoon, Ottawa’s electric lights had also blinked; that time twice on news that Kaiser Wilhelm II had abdicated. Within minutes, the streets were a mass of exultant people, celebrating the end of the “Beast of Berlin,” and the overthrow of the House of Hohenzollern. Vehicles of all descriptions, flivvers, touring cars, tractors, and trucks, many decorated with flags and pennants, and loaded with people, slowly made their way down Sparks Street. The noise was deafening. In addition to horns, tin whistles, and the beat of pots and pans, some automobile owners had attached whistles to “cut outs” in their car exhaust pipes adding still more decibels to the cacophony. That evening, a mob of celebrating young people paraded through the revolving doors of the Château Laurier Hotel, past the statue of Sir Wilfrid Laurier in the rotunda, and into the dining room, to the applause of diners. Shortly after 11pm, an effigy of Kaiser Bill, decorated with pictures of Grand Admiral von Tirpitz, the instigator of unrestricted submarine warfare, the Austrian Emperor, and the German Crown Prince, was burnt on Connaught Square. The effigy had been made by the Citizen press-room staff using oil-soaked rags and waste. It was set alight by Chief Graham of the Ottawa Fire Department. The crowds started to disperse after midnight to await news that peace had arrived.
An armistice had been expected the following day. But Sunday came and went without an announcement. Nonetheless, plans for the big day went ahead. Ottawa’s Mayor Fisher announced that the day of the armistice would be a public holiday. A “monster” parade was scheduled. A request went out for all car owners to decorate their vehicles with flags of allied nations, and join the parade. Along with the war veterans and members of the 2nd Battalion stationed at Lansdowne Park, the letter carriers would parade in uniform. The pipe band of the St Andrew’s Society was also requested to gather for the march on Parliament. Kiwanis Club members were asked to form up at the entrance to Parliament Hill close to Bank Street. A series of floats were also planned, including one of a boat on which the Kaiser was on his knees tied to a winch.
When the news finally broke in the wee hours of Monday morning, the city went wild; the ensuring celebration far outstripped anything two days earlier. As the Citizen noted, Saturday’s celebrations merely marked the passing of a murderer and tyrant, while Monday’s “was a celebration of the greatest victory for civilization in the history of the world.” After the city’s lights flashed, Ottawa residents were summoned to the streets by the sound of fire station gongs and sirens, factory whistles, and church bells. In these days before radio, telephone girls quickly spread the word across telephone exchanges. Whole families, tousled haired and hastily dressed, stumbled out onto the early-morning streets waving flags or pennants, and blowing tin horns. The Postmaster-General, Lieutenant-Col. Hon. Pierre-Édouard Blondin was in his home library on Range Road when his electric lights blinked. Immediately, he and his family got dressed and drove in their car to Sparks Street where they found themselves at the head of an impromptu parade of celebrating citizens.
At 3.10am, the Citizen posted the new bulletin “GERMANY SURRENDERS” on their Sparks Street office window, eliciting prolonged cheers from the growing throng outside. A short time later, the skirl of bagpipes could be heard over the din, emanating from the corner of O’Connor and Slater Streets, followed by the sound of drums and horns of the “Victory Loan” and G.W.V.A. (Great War Veterans’ Association) bands that had quickly assembled. Making their way to Parliament Hill, they played “Maple Leaf Forever,” with thousands of voices joining in the song. After the last chorus, the bands struck up the famous tune of the “Old Hundred,” to which the crowd sang “Praise God From Whom All Blessings Flow.” After a moment of silence, an immense cheer went up that lasted for more than two minutes. The massed bands and then played another old church favourite “Our God Our Help In Ages Past.” As dawn approach, Reverend (Major) T. Thompson gave a concluding prayer. Afterwards, the bands struck up some familiar tunes, followed by the National Anthem, and, finally, “Tipperary,” in tribute to the boys a long way from home in the trenches in France and Belgium. Unabashed tears ran down the cheeks of many as they sang.
The Ottawa Citizen described the scene as one of “extreme beauty.” Above the heads of the crowds, stars sparkled, with a faint hint of dawn in the east. Over at Connaught Square, the lights illuminating the Victory Loan campaign, which included a huge promotional “cash register,” twinkled, giving the appearance of a “fairy spectacle.” High in the sky, the large electric sign mounted on top of the Château Laurier Hotel read “Victory” instead of “Buy Victory Bonds,” thanks to a quick-thinking hotel electrician. On Wellington Street, a bonfire cast an orange, flickering glow on the surrounding buildings and the milling crowds. The partying continued through the day. Stores, decorated in flags and bunting, experienced a run on Allied flags. One shop even sold out of old Diamond Jubilee Flags, bearing an image of Queen Victoria, left over and almost forgotten from the 1897 festivities.
The official celebrations began at 2pm that afternoon with more than 10,000 people assembled on Parliament Hill. In a huge parade, veterans and the G.W.V.A. band, directed by Lieutenant Jones, assembled on Cartier Square, and marched to the Hill. There, the “vets” met up once again with the “Victory Loan” band, conducted by Sergeant Cook, in front of the new Centre Block, still being rebuilt after the disastrous fire of 1916. On either side of the steps leading up to the building were soldiers representing the allied nations holding their flags. At 2.30, the official party arrived, including the Governor General and his wife, the Duke and Duchess of Devonshire, Lady Borden, the wife of the Prime Minister (Sir Robert Borden was in England at the time), Hon. Newton Rowell, the President of the Privy Council, as well as senior religious and military leaders.
After being introduced by Mr Rowell, the Governor General spoke of the major role played by Canadian troops in achieving victory, and how glad he was to be in Canada and “share in the pride that Canada had every right to feel.” He added “the Empire would never forget the deeds of its soldier sons, on land, in the air, and on the seas.” He concluded by saying that “we have laid the foundation for a long peace.” Although the Governor General was wildly cheered, the newspaper reported that his speech was difficult to hear owing to “small boys extracting horrible sounds from tin horns.” After prayers of thanksgiving offered by the clergy, the two bands reprised the hymns that they had played earlier in the morning in the spontaneous celebrations that had occurred immediately follow news of the armistice. The official ceremonies concluded by a speech from Rowell who spoke of the “debt of gratitude” owned by the nation to those who sacrificed their lives for the Empire in the fight for civilization. He also read out to the cheering crowd the armistice terms signed by Germany. The proceedings ended with a rousing rendition of “Rule Britannia.”
That evening, a special Thanksgiving service was held at St Bartholomew’s Church with the Governor General reading the lesson. The following day, 12 November, another Thanksgiving service was held at Christ Church Cathedral at noon. Among the congregation were the Duke and Duchess of Devonshire, Sir Wilfrid Laurier, and Lady Borden. Later that day, members of the Ottawa Motor Club assembled at the corner of Wellington and Bank Streets for the “Great Victory Parade” down Rideau, Bank, and Sparks Streets.
Sadly, as we all know, the Governor General’s hope that the war had laid the foundation for a lasting peace was not fulfilled. Twenty-one years later, a new generation of Canadian soldiers were called to arms.
Sources:
The Ottawa Citizen, 1918. “PEACE!,” 11 November.
————————, 1918. “When Peace Comes Ottawa Will Have Full Celebration, 11 November.
———————-, 1918. “Ottawa Joyfully Celebrated The News Of The Kaiser’s Abdication, 11 November.
———————–, 1918. “Ottawans Joined In Celebrations As Never Before,” 12 November.
The Ottawa Journal, 1918. “The Auto Parade,” 12 November.
———————–, 1918. “People’s Victory, Says Bishop Roper,” 12 November.
———————–, 1918. People Of Capital Celebrate Twenty-four Hours, 12 November.
Story written by James Powell, the author of the blog Today in Ottawa's History.
Retired from the Bank of Canada, James is the author or co-author of three books dealing with some aspect of Canadian history. These comprise: A History of the Canadian Dollar, 2005, Bank of Canada, The Bank of Canada of James Elliott Coyne: Challenges, Confrontation and Change,” 2009, Queen’s University Press, and with Jill Moxley, Faking It! A History of Counterfeiting in Canada, 2013, General Store Publishing House, Renfrew, Ontario. James is a Director of The Historical Society of Ottawa.















